Identical (Monozygotic) Twins – What Are They & How They Are Formed

- What Are Identical Twins?
- How Are Monozygotic Twins Formed?
- What Increases the Chances of Having Twins?
- Why Does a Fertilised Egg Split Into Two?
- When Are Monozygotic Twins Actually Formed?
- How Do You Know If Your Twins Are Identical?
- Are Ultrasound Scans for Confirming Identical Twins Accurate?
- More Facts About Identical Twins
- Misconceptions About Monozygotic Twins
- FAQs
Twins are nature’s wonder. Their birth also involves special pre-natal and post-natal preparations to avoid complications. Accurate knowledge about them prepares for their arrival and aftercare. The first thing you need to know is that they broadly come under two categories – identical and non-identical twins.
- Identical (monozygotic) twins are also called non-fraternal twins. They result from the fertilisation of a single egg that splits in two. One in every three sets of twins is identical.
- Non-identical (dizygotic) twins are also called fraternal twins. They grow from two separate zygotes. They form 2/3rd of the twin population.
This article aims at providing you with ample information about identical twins to make it easy for you to manage your pregnancy and prepare yourself for the upcoming parenthood. Let’s begin with understanding identical twins a little in-depth.
What Are Identical Twins?
Identical twins share the same DNA and often look alike. Medically, they are called monozygotic because these twins develop from one (mono) zygote (fertilized egg) (1).
How Are Monozygotic Twins Formed?
Identical or monozygotic twins are formed when one sperm fertilises one egg to form one zygote, which then splits into two separate embryos that develop into two foetuses in the same womb (2). This phenomenon is observed in natural as well as assisted pregnancies. In assisted pregnancy, if one fertilised egg is returned to the mother’s uterus, the egg may divide and produce identical twins in the womb.
So, why does the fertilised egg split into two? We’ll get to that after knowing what possibly increases the chances of having twins.
What Increases the Chances of Having Twins?
Some women are likely to have a higher chance of giving birth to twins. This happens because (3):
- Diet: Excessive dairy and meat have been known to increase the chances of having twins. In addition, food items like bananas and asparagus, which are known to improve fertility, can also make you have twins.
- Family Size: Having twins can sometimes just be a number game. The odds of having twins are slim, but if you keep having kids, some of them are bound to be twins.
- Pills: Fertility pills can overstimulate the ovaries and lead to multiple eggs being produced at a given time.
- Maternal Age: Women in their late thirties tend to produce more follicle-stimulating hormones. This results in situations where more than one egg is produced in a single cycle.
- Family History: Having multiple twins on either side of the family can be a factor for having twins. It may be indicative of the women in the family having an ovarian abnormality of producing multiple eggs in a single cycle.
Why Does a Fertilised Egg Split Into Two?
Medical science has still not exactly identified why this happens despite much research. One may, at best, say that it is actually a malformation during pregnancy. According to some research, less than 20 families have been reported with a genetic 50% likelihood of getting pregnant with twins. Another research suggests that the womb environment in identical-twin pregnancy triggers the zygote split in many cases.
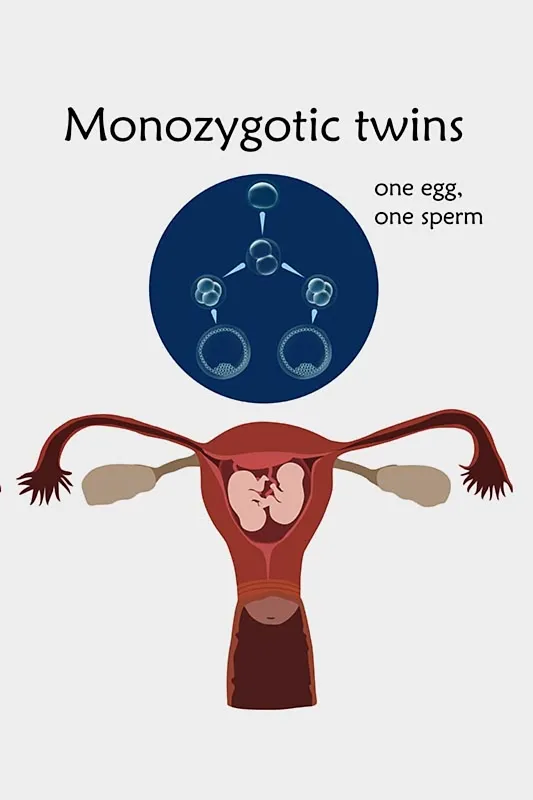
When Are Monozygotic Twins Actually Formed?
Identical twins are usually formed when the zygote is in the very first phase of development. At this time, the zygote splits into two separate embryos that form two foetuses that go on to become identical twins. This causes each baby to have the same genetic information.
How Do You Know If Your Twins Are Identical?
It is not easy to know whether your twins are identical. An ultrasound may come up with some indications that characterise it, though (4):
- They have developed from one fertilised egg or two.
- They share a placenta.
- They have the same gender (although in many countries, determining this may be legally forbidden).
Are Ultrasound Scans for Confirming Identical Twins Accurate?
An ultrasound scan is not a foolproof method to confirm identical twins. Some identical twins may split during the early stages and develop with two placentas, thereby developing as non-identical twins. These may not be detected by an ultrasound. Advanced pregnancy examinations like amniocentesis or Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS) may be more accurate.
More Facts About Identical Twins
There are a few more things you should know about identical twins:
1. There are generally three types of identical twins. One-third of them have separate placentas, two-thirds share a placenta and are called monochorionic, and very few of them share an inner sac, called the amnion, in addition to sharing a placenta. The ones who share an inner sac are called monoamniotic (MoMo).
2. There is another type of monozygotic twins with opposite features. They are called mirror twins. They have the same DNA, and one of the twins may also have organs placed on the opposite side of the body. For instance, the heart may be on the right side.
3. Half-identical twins or Polar Body Twins are the twins that are born when an egg splits before fertilisation, and each half is fertilised by separate sperm (5). Polar Body Twins are known to share 75% of their DNA and have not been officially accepted as twins.
4. There are only three documented cases of identical twins with opposite sexes, and they are because of chromosomal birth defects.
5. Identical twins may suffer from Vanishing Twin Syndrome, wherein one of the twins disappears in the uterus due to a miscarriage. Following this, the foetal tissue gets absorbed by the other twin, placenta or the mother.
6. Many women have miscarriages of one twin early in their pregnancy, but the other survives. This is similar to vanishing twins.
7. Identical twins can be conjoined twins (Monoamniotic-Monochorionic). These twins have bodies that are joined together at birth (6). Conjoined twins are very likely to be mirror twins.
8. Sometimes one twin foetus does not develop at all and becomes a parasite of the other. These are called parasitic twins.
9. Chimaeras are individuals who may have parts that they have received from an identical twin in the womb.
10. There is an illness called Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS) that impacts identical twins. This is a placental disease where fluid distribution is uneven and affects the twins differently. While one becomes dehydrated, the other becomes inundated with fluid leading to excessive urination.
11. Lastly, these peculiarities also indicate that identical twin pregnancy should be properly discussed with your doctor to ensure smooth delivery because they are prone to complications.

To understand the phenomenon better, you must also be aware of the misconceptions about identical twins. Some knowledge about them can also help you tackle the questions coming your way when you have your babies.
Misconceptions About Monozygotic Twins
Here are the most common myths about identical twins:
- Identical twins mean exactly the same: This happens because it is assumed that identical twins have the same characteristics due to the same DNA they share.
- Identical twins have the same height and weight at birth: This comes from the same inference that identical twins have everything similar because they share the same DNA.
- Doctors always know that it is an identical twin: A doctor cannot be conclusive and say for sure whether you are carrying identical twins because there are many peculiarities among twins that examinations may not be able to identify.
- Hairline/parts are all identical: This is the most common assumption because no one has the knowledge that identical twins can be very different from each other.
- Personalities of identical twins never differ: This is the biggest myth of all! Almost always twins have unique character traits.
- Parents of identical twins will never get confused about their twins: Why not? It is natural to do so if they really look the same!
- It is very important to know whether you have an identical or fraternal twin: It is not necessary at all to know so much, and this will not pose any problems on how you bring them up.
FAQs
1. Can identical twins be of different genders?
Identical twins are always of the same gender because they always have the same DNA. However, there have been exceptions where the gender of the two babies was different.
2. Will it be obvious that twins are identical at birth?
Most times, it will be obvious at birth whether the twins are identical or fraternal. However, there are ways to confirm this (in case you have a doubt). An ultrasound scan in the first trimester of pregnancy could throw some light on whether they are identical twins. It is best to do this scan before 14 weeks of pregnancy because it is easier to see whether the twins are sharing the placenta, which identical twins do in most cases.
Sometimes, there is some confusion whether it is an identical or fraternal twin because some identical twins could be born with separate membranes. A DNA test could clear the confusion.
3. Difference between identical and fraternal twins
Some of the key differences between identical and non-identical twins are:
- Identical twins share the same DNA, while fraternal twins share around half of it.
- Identical twins could sometimes look different, while fraternal twins mostly always look different.
4. Can identical twins have different fingerprints?
Yes! Even though identical twins share nearly identical DNA, their fingerprints develop differently due to slight variations in the womb (like amniotic fluid movement and umbilical cord position). Fingerprints are influenced by both genetics and environmental factors during fetal development.
5. Do identical twins always share the same blood type?
In rare cases, no. While most identical twins have the same blood type, chimerism (where two fertilised eggs fuse early in development) or somatic mutations can lead to slight differences in blood type or other genetic traits.
These were some amazing identical twins facts. Now that you know a lot about identical twins, we wish you the very best in your twin journey with them!
References/Resources:
1. National Human Genome Research Institute – Identical Twins
2. Better Health Channel – Twins – identical and fraternal
3. The Ohio State University – What increases the odds of having twins?
4. American Academy of Pediatrics – The Difference Between Identical and Fraternal Twins
5. ICOMBO – Zygosity for twins
6. Mayo Clinic – Conjoined twins
Also Read:
Fraternal Twins
Mirror Image Twins
Twin Pregnancy Types
Was This Article Helpful?
Parenting is a huge responsibility, for you as a caregiver, but also for us as a parenting content platform. We understand that and take our responsibility of creating credible content seriously. FirstCry Parenting articles are written and published only after extensive research using factually sound references to deliver quality content that is accurate, validated by experts, and completely reliable. To understand how we go about creating content that is credible, read our editorial policy here.




































