Parts of a Plant – Interesting Facts for Kids
Plant life is an integral part of nature. There are many kinds of plants, bushes and trees in our surroundings. They play an essential role in our daily lives by providing us with the oxygen we breathe, the food we consume, medicine, paper, rubber products, fuel, shelter and clothing. But have you ever wondered how plants grow and function? Just like humans have different body parts that perform specific tasks, plants also have unique parts, each with an important role. In this article, we’ll explore the list of all parts of a plant and their functions, as well as some fascinating facts that will amaze young learners!
Structural Classification of a Plant
Plants are unique in terms of physical appearance, physiological behaviour, and structure. So, with that kind of diversity, it is important to teach kids about their basic structural classification so that they get excited about a plant’s journey from seed to plant. Flowering plants look attractive and help to uplift our mood. If your kid is interested in flowers, enlighten them all about the parts of a flowering plant so that they know that flowers are special structures that not only spread sweet fragrance but are involved in pollination and fertilisation as well. Given below is the diagram of parts of a plant:
1. The Root
The part of the plant that is hidden underground is called the root system. It consists of organs like roots, tubers and rhizomes. Roots hold the plant/tree steady in the ground, absorb water and minerals from the soil.
2. The Shoot
Shoots are located above the ground and include organs such as the leaves, stem, flowers (for flowering plants) and fruits (plant bearing fruits). They help plants make their food by the process of photosynthesis.
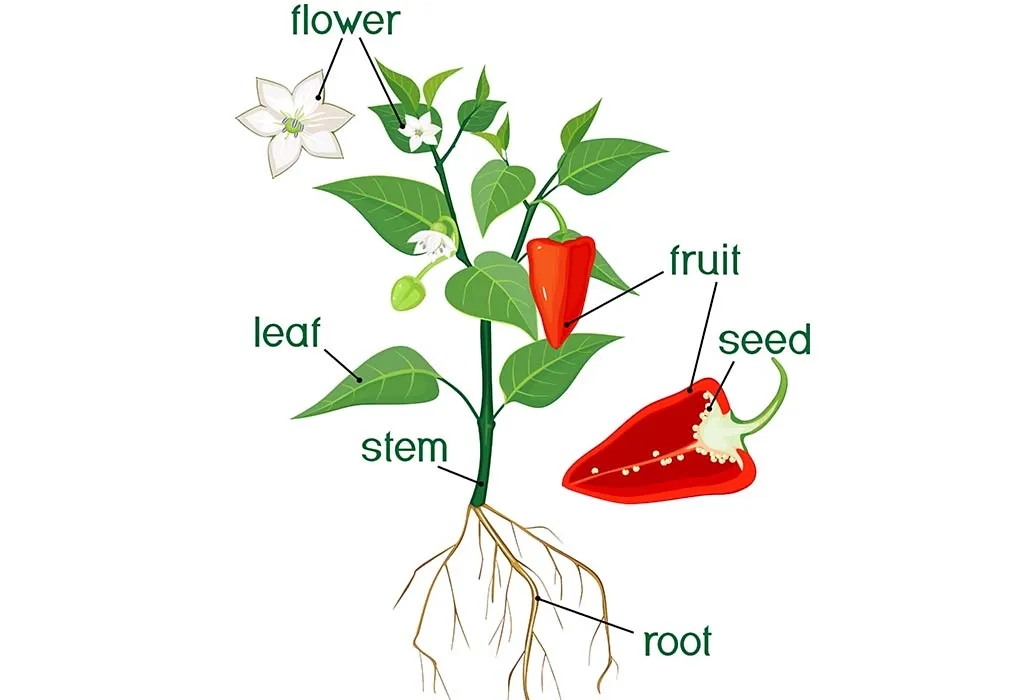
List of All Parts of a Plant and Their Functions
Many children often ask, “What are the six main parts of a plant?” when learning about nature and how plants grow. To answer this, let’s explore the amazing plant parts and functions.
1. Root
Roots are simple tissues that are derived from the stem of the plant. They absorb moisture and essential nutrients from the soil. They also help to anchor the plant to the ground and support the stem of the plant. In some plants like carrots, roots store food, while in some, they are used for propagation (1).
2. Stem
The primary function of a stem is to transport the water and nutrients from the roots and distribute them to the leaves to be converted into food through photosynthesis. The stem also transports the food from the leaves to the plants’ other parts, including the roots. Stems store food, water, etc., for the plant and, if they are green, generally produce food themselves. They also support the leaves as well as the other reproductive structures (2).
3. Leaf
A leaf is the part of the plant that makes food for the plants by the process of photosynthesis. It traps energy from the sunlight and uses it to convert the air and water into glucose. The presence of chlorophyll in leaves give them their green colour, and chlorophyll is responsible for absorbing light energy from the sun. The leaves also help to identify the type of plant species it belongs to (3).
4. Fruit
Fruits are the part of flowering plants that contain and protect the tiny developing seeds within them. Fruits also help in the dispersal of seeds and are the edible part of the plant for humans (4).
5. Flower
This reproductive organ of a flowering plant makes seeds that become new plants. Flowers also attract pollinators that help with the fertilisation process of the plant and results in fruits. They can also be a rich source of food for living organisms like humans, birds and animals.
6. Seed
Seeds are the reproductive parts of a plant that are packed with nutrition. They grow into new plants after being sown into the ground (5).
Some Amazing Facts About Part of Plants for Children
Plants are full of surprises! Each part of a plant has a special role, and some of them have unique and fascinating abilities. Here are some amazing facts about different plant parts that will amaze you:
1. Plant roots always grow downward because they can sense gravity, helping them find water and nutrients in the soil.
2. Cacti have thick, fleshy stems that store water, allowing them to survive in hot and dry deserts.
3. Brightly coloured flowers and sweet scents attract bees, butterflies, and birds, which help plants reproduce by carrying pollen.
4. Fruits act like a protective covering for seeds and help in their dispersal when animals eat them and drop the seeds elsewhere.
5. Some seeds remain dormant for years before they sprout, waiting for the right conditions to grow into plants.
6. Tiny openings called stomata on leaves allow plants to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen into the air.
7. Plants like mangroves and orchids have roots that grow above the ground or in the air to absorb moisture and nutrients.
8. Bamboo is a type of grass with a strong, hollow stem that can grow incredibly fast, up to 3 feet in a day!
FAQs
1. Why do leaves change colour in autumn?
During autumn, some trees stop producing chlorophyll (the green pigment in leaves), revealing other colours like red, yellow, and orange. This process helps trees prepare for winter (6).
2. Can plants live without soil?
Yes! Some plants, like hydroponic plants, grow in water with added nutrients instead of soil (7). Air plants (Tillandsia) absorb nutrients from the air and don’t need soil at all!
Classrooms that contain plants can positively contribute to the psychological well-being and development of children. Try some creative ways to teach your kids more about plants so that they appreciate their contribution to human existence.
References/Resources:
1. Stanford University – The structure and function of root systems
2. The Huntington Library, Art Museum, and Botanical Gardens – Stems
3. The Huntington Library, Art Museum, and Botanical Gardens – Leaves
4. Encyclopedia Britannica – fruit
5. Encyclopedia Britannica – seed
6. Encyclopedia Britannica – Why Do Leaves Change Colors in the Fall?
7. U.S. Department of Agriculture – Hydroponics
Also Read:
Sun Facts for Children
Earth Facts for Children
Science Facts for Children
Was This Article Helpful?
Parenting is a huge responsibility, for you as a caregiver, but also for us as a parenting content platform. We understand that and take our responsibility of creating credible content seriously. FirstCry Parenting articles are written and published only after extensive research using factually sound references to deliver quality content that is accurate, validated by experts, and completely reliable. To understand how we go about creating content that is credible, read our editorial policy here.













.svg)
















