Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) Infection – Could Your Child Be at Risk?

- What Is Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
- How Common Is Human Metapneumovirus?
- Who Is at Risk of Getting an HMPV Infection?
- Is Human Metapneumovirus Contagious?
- How Is HMPV Transmitted?
- Risk Factors for HMPV Virus Infection
- HMPV Symptoms
- HMPV Vs COVID
- Is Human Metapneumovirus Infection Same as Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- What Are the Complications of Human Metapneumovirus?
- How Long Does It Take to Recover From Human Metapneumovirus?
- Diagnosis
- Treatment for HMPV Infection
- How to Prevent HMPV?
- Protecting Your Child From HMPV
- Is There Any Case of HMPV Detected in India?
- When to Seek Medical Help?
- Questions to Ask Your Doctor
- FAQs
There are certain viruses that share similar traits but aren’t the same. Symptoms like wheezing and nasal congestion are often informally diagnosed as a cold or a flu. Human metapneumovirus, or HMPV, is a virus that causes acute respiratory infections in people similar to a common cold or RSV (1). The viral infection tends to circulate rapidly during spring and winter, coinciding with the spread of other respiratory infections, like flu or RSV. Even though the symptoms are mild and mimic flu and COVID-19, there is a difference, which makes it essential for parents to be aware of this infection.
Expert Says
“At present, there’s nothing to panic as the virus has been in circulation since long, and the symptoms are similar to other respiratory viruses. Take the precautions, especially in children below 5 years, and visit your doctor when any symptoms arise.“
– Dr. Gunjan Baweja (Pediatrician)
What Is Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
Human metapneumovirus, commonly known as the HMPV virus, is a single-stranded RNA virus from the Paramyxoviridae family, which often causes upper respiratory infections, and in some cases, elevates lower respiratory infections, such as flaring up of asthma, worsening chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or pneumonia. HMPV belongs to the same group of viruses that cause respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and measles and mumps, but they are not the same.
HMPV infections are commonly observed in the early spring and winter. It is important to note that most individuals get HMPV infection before the age of 5. According to the Cleveland Clinic, children experiencing the HMPV infection the first time are more likely to develop severity than those getting it again. This is one of the reasons young babies and children are at a high risk of developing serious illness (5). Since it is a communicable infection, infants, young children, and adults can get it again, but the severity reduces in the subsequent infections.
How Common Is Human Metapneumovirus?
According to the Cleveland Clinic, HMPV is responsible for about 10 to 12% of respiratory diseases in children. While most cases are mild, about 5-16% of children have a chance of developing lower respiratory infections like pneumonia or bronchiolitis.
Who Is at Risk of Getting an HMPV Infection?
While HMPV infection affects both children and adults, it is commonly seen in children below the age of 5. Thus, young children, adults over the age of 65, and individuals with weakened immune systems are the most vulnerable to contracting severe HMPV infection.
Is Human Metapneumovirus Contagious?
Yes, human metapneumovirus is highly contagious, similar to cold and RSV. The incubation period of HMPV is about three to five days. This means a person may be contagious even if they don’t show any symptoms yet (7).
How Is HMPV Transmitted?
HMPV is easily transmitted in children and adults by coming in direct contact with the mucus or saliva of the infected person or touching things or surfaces contaminated with the virus (1).
Instances include:
- Breathing in droplets when the infected sneezes or coughs on them
- Shaking hands, kissing, or hugging
- Sharing utensils or food
- Touching keys, door handles, toys, sports equipment, phones, tissues, or menu cards contaminated with the virus

Risk Factors for HMPV Virus Infection
HMPV is a common virus that can infect anyone in general. Nevertheless, the quantum of risk factors in children, particularly young children and infants, is high, and it is more likely to develop into severe respiratory conditions, like pneumonia, bronchitis, or bronchiolitis. The following categories are at a high risk of developing severe illness due to human metapneumovirus:
- Premature infants
- Young children under 5
- Elderly people above the age of 65
- People with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Individuals with weakened immune systems (such as those battling autoimmune disorders, cancer, or HIV, having medications that suppress the immune system, or recovering from organ transplants)
HMPV Symptoms

Metapneumovirus symptoms are usually mild and cold-like but can cause various symptoms that range in severity. Since the infection primarily infects the lungs and airways, some people may experience a flare–up due to their weakened immunities.
The symptoms of HMPV include:
- Cough
- Runny or stuffy nose (cold)
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Rash
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Wheezing
Fever and runny nose usually begin three to five days after contracting HMPV infection. If it persists, children may develop other symptoms like wheezing, cough, and shortness of breath. For infants and young babies below the age of 6, the infection could manifest as severe respiratory distress, along with the symptoms of apnea.
Also Read: Ways to Increase Immunity in Children
HMPV Vs COVID
Human metapneumovirus and COVID-19 are respiratory illnesses with similar symptoms, like coughing, a runny nose, nasal congestion, fever, sore throat, and shortness of breath. Both are contagious and usually spread in the same fashion through close contact with people or touching contaminated surfaces or things. In serious cases, both infections could lead to hospitalization. However, there are some differences, which are as follows:
- Unlike COVID-19, human metapneumovirus does not have a specific antiviral medication or vaccines.
- While HMPV is seasonal and mostly prevalent during spring and winter, COVID-19 is annual due to the circulation of new variants year-round.
It has come to notice that the cases of HMPV have increased three-fold in some countries after the COVID-19 pandemic. Due to preventive measures like quarantine, the transmission of various respiratory infections was reduced, but after the ease of preventive measures, infections like HMPV surged.
Is Human Metapneumovirus Infection Same as Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
HMPV and RSV belong to the same genus and can result in similar symptoms. However, they are not the same. While HMPV causes severe illness in babies aged between 6 and 12 months, RSV typically causes severe illness in infants and young babies under 6 months.
What Are the Complications of Human Metapneumovirus?
The complications and risks in kids, particularly infants and those under the age of 5, are higher than in older children and individuals. While the HMPV infections are usually mild, children and vulnerable classes may progress to more serious conditions and lead to hospitalization. The complications include (10):
- Pneumonia
- Bronchitis
- Bronchiolitis
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
- Ear infection (otitis media)
How Long Does It Take to Recover From Human Metapneumovirus?
A majority of HMPV cases are mild and last a few days to a week. If the infection is slightly severe, it may take a little longer to recover. Symptoms like cough may linger for some time.
Also Read: Immunity Boosting Foods for Kids
Diagnosis
To diagnose HMPV infection, the doctor will take note of your physical symptoms and health history. They might take a sample from your nose or throat and order a swab test along with other lab tests to confirm the identity of the virus causing the infection. Tests are usually not done unless doctors identify the severity or the need for hospitalization. Individuals showing severe or persistent symptoms may be recommended a bronchoscopy or a chest X-ray to check the situation of airways in the lungs and detect viruses.
Treatment for HMPV Infection
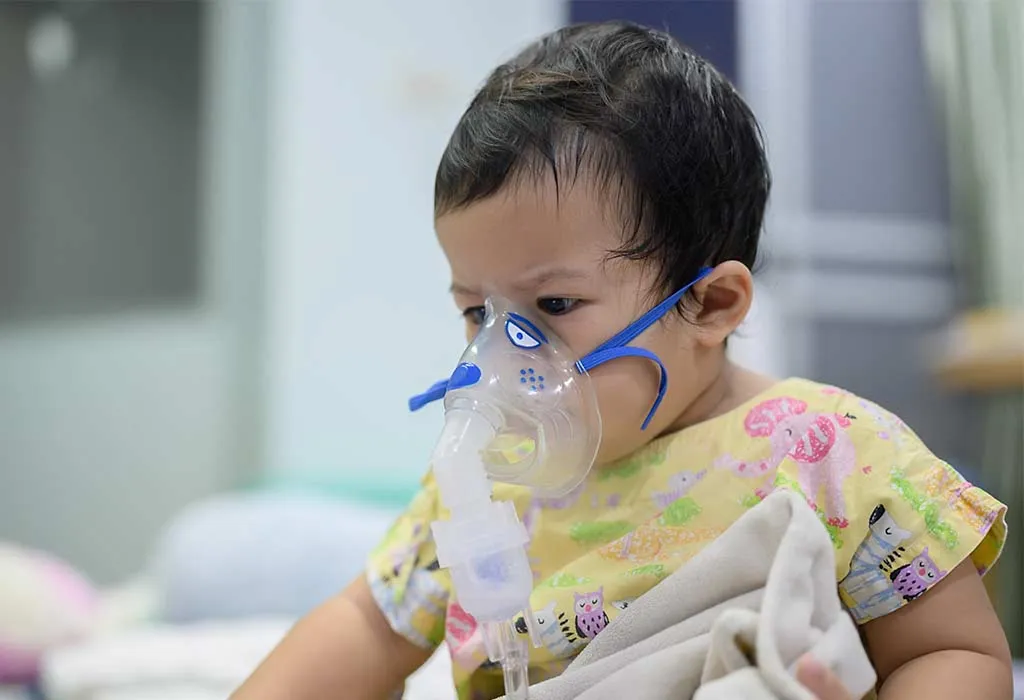
There is no specific antiviral medication that offers metapneumovirus treatment. Since most HMPV cases are mild and go away on their own, doctors recommended symptomatic care to manage the symptoms and prevent flare-ups, such as:
- Over the counter (OTC) medications, such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen, to control fever and pain
- Decongestants for nasal congestion
- Inhaler for wheezing and coughing
If the child is severely ill and experiencing breathing problems, they may be hospitalized. Healthcare professionals may provide:
- IV fluids: The infection’s symptoms, like fever and cough, can cause dehydration. Doctors may recommend the administration of IV fluids to keep the patient hydrated.
- Oxygen Therapy: Doctors may provide extra oxygen through a tube or mask for children or individuals having breathing difficulties.
- Corticosteroids: Steroids are often used to reduce inflammation in the body.
How to Prevent HMPV?
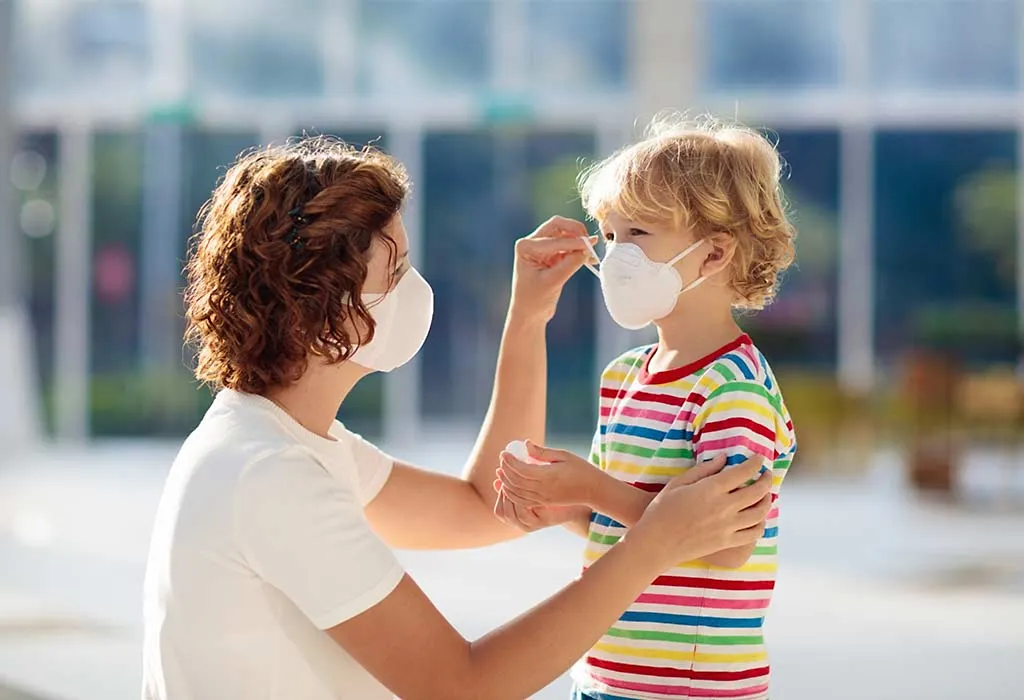

There is no vaccine to prevent human metapneumovirus (HMPV) infection. Since it transmits like other viral infections through close contact, there are some ways to prevent its spread and reduce the getting the HMPV infection.:
- Avoiding contact with infected people and maintaining distance from them.
- Washing hands thoroughly with soap and water for at least 20 seconds. If soap isn’t available, an alcohol-based sanitizer can be used.
- Covering the nose and mouth with a tissue, handkerchief, or your elbow—and not your bare hand — when sneezing or coughing.
- Wearing a face mask when in public areas or crowded spaces.
- Avoid frequently touching your face, mouth, nose and eyes with bare hands.
- Refraining from sharing food or eating together in or with the same utensils with others.
- Ensuring all the vaccinations are up to date.
Also Read: How to Boost Baby’s Immunity System?
Protecting Your Child From HMPV
To ensure your child remains safe and protected against the viral HMPV virus, make sure of the following:
- Ensure they wash their hands thoroughly before and after eating as well as after visiting the washroom and coming from outside.
- Keep them hydrated by offering them plenty of fluids, like water and electrolytes.
- Refrain from taking your child to crowded places.
- Limit their contact with infected people, either in the family or outside.
- Make sure you take all hygiene precautions, as you could act as a silent infection spreader and infect your child even if you don’t show any symptoms.
Is There Any Case of HMPV Detected in India?
Recently, India has seen a few of HMPV incidences. Noted by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), the cases were found at Karnataka’s Bengaluru’s Baptist Hospital. The situation has been closely monitored by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. According to the Union Ministry, the surveillance mechanisms are in place, which currently indicates no unusual surge in cases.
The Ministry has urged people to follow basic hygiene practices and eat healthily to stay safe and fit during the winter season.
When to Seek Medical Help?
In a majority of cases, medical intervention is not needed since the infection goes away in a few days to a week with symptomatic care. However, if the symptoms worsen or your child develops the following conditions, you must seek immediate medical attention:
- High fever
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Severe cough
- Bluish skin, lips, or nails
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
As an informed parent, you can ask the following questions about human metapneumovirus in kids:
- How do I treat HMPV infection at home?
- How long will it take for my child to feel better?
- What over-the-counter medications are safe for my child?
- Which severe symptoms should I be aware of?
- When should I go to the emergency room?
FAQs
1. Are antibiotics required for treating human metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
No, antibiotics are not required for treating HPMV as they only treat bacterial infections. Since human metapneumovirus causes a viral infection, antibiotics won’t be of use. In some cases, infected individuals may develop secondary infections like a bacterial infection the same time they get pneumonia from HMPV. In those situations, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics to treat any secondary infections.
2. How long does it take to recover from the HMPV virus?
Mild HMPV infections take about three days to a week to recover, and symptoms like cough could last longer. If the infection persists for more than a week, please contact your doctor.
3. Can you get HMPV infection more than once?
Yes, it is possible to get HMPV infection twice or more than once. In subsequent infections, the severity reduces, and the infection gets milder as the body builds immunity to it.
People with chronic respiratory diseases, such as asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, or COPD, remain at high risk of contracting infections like HMPV or influenza.
References/Resources:
1. Human metapneumovirus fact sheet; NHMRC; https://www.nhmrc.gov.au/about-us/publications/staying-healthy-guidelines/fact-sheets/human-metapneumovirus
2. Abdullah Brooks. W, et al.; Human metapneumovirus infection among children, Bangladesh; Emerging Infectious Diseases; PubMed Central; https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2851498/; October 2007
3. Principi. N, et al.; Human metapneumovirus in paediatric patients; Clinical Microbiology and Infection; https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1198743X14615962; April 2006
4. Holzemer. N. F, et al.; Human Metapneumovirus Infection in Hospitalized Children;
5. Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV); Cleveland Clinic; https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22443-human-metapneumovirus-hmpv
6. Heikkinen. T, et al.; Human metapneumovirus infections in children; Emerging Infectious Diseases; PubMed Central; https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2600144/; January 2008
7. Human Metapneumovirus; IDPH; https://dph.illinois.gov/topics-services/diseases-and-conditions/diseases-a-z-list/human-metapneumovirus.html
8. Simon. A, Manoha. C, Müller. A, et al.; Human Metapneumovirus and Its Role in Childhood Respiratory Infections; Current Pediatrics Reports; https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40124-014-0048-6; May 2014
9. Edwards. K. M, et al.; Burden of Human Metapneumovirus Infection in Young Children; The New England Journal of Medicine; https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1204630; February 2013
10. Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) Symptoms and Diagnosis; American Lung Association; https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/human-metapneumovirus-hmpv/symptoms-diagnosis
11. Bhatia. R; Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection and Human Metapneumovirus Infection; MSD Manual; https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/children-s-health-issues/respiratory-disorders-in-infants-and-children/respiratory-syncytial-virus-rsv-infection-and-human-metapneumovirus-infection
12. Kimberlin. D, et al.; Human Metapneumovirus; Red Book: 2021–2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases (32nd Edition); American Academy of Pediatrics; https://publications.aap.org/redbook/book/347/chapter-abstract/5754213/Human-Metapneumovirus?redirectedFrom=fulltext; 2021
13. About Human Metapneumovirus; CDC; https://www.cdc.gov/human-metapneumovirus/about/index.html
Also Read:
Viral Infection in Kids
Cold vs Flu in Children
Dengue Fever in Kids
Malaria in Children
West Nile Virus in Kids
Chikungunya in Children
Zika Virus Infection in Kids
Rubella (German Measles) in Babies and Kids
Chandipura Virus – How to Protect Your Child!
Was This Article Helpful?
Parenting is a huge responsibility, for you as a caregiver, but also for us as a parenting content platform. We understand that and take our responsibility of creating credible content seriously. FirstCry Parenting articles are written and published only after extensive research using factually sound references to deliver quality content that is accurate, validated by experts, and completely reliable. To understand how we go about creating content that is credible, read our editorial policy here.













.svg)


















