How to Make Your Premature Baby Gain Weight?

A premature baby, also called a preemie, needs to overcome several obstacles to become healthy. As the mother or the caregiver, you must be extra careful and ensure your baby gets optimum nourishment. Adequate weight gain is crucial for their overall health and development, as it helps them build strength and resilience. While premature babies may face unique obstacles compared to full-term infants, there are various strategies and approaches parents can employ to support their little one’s weight gain journey. However, before you decide on a weight-gain plan for your baby, let’s look at what a premature baby is and how much such a baby weighs.
Who Is a Premature Baby?
A baby born before 37 weeks of gestation is considered a premature baby (7).
How Much Weight Do Premature Babies Generally Gain?
Monitoring preterm weight gain is crucial for ensuring the healthy development of premature infants. Three kg is the approximate birth weight for full-term babies. The premature baby’s weight gain per day depends on when the baby is born. The earlier the delivery is, the less the baby will weigh. Premature babies usually have a birth weight of less than 2.3 kg (5).
Extremely low birth weight in babies can pose a severe risk to their survival. More than 90% of preemies weighing 800 gm or more can survive due to medical advancements. These days, around 60% of premature babies weighing more than 500 gm survive (3).
All newborns follow a pattern as far as weight gain is concerned. They usually lose some weight during the initial few days. This weight loss could be due to a variety of factors. Babies who have just been delivered might have retained some fluids if the doctor administered a hormone drip to the mother to speed up labour. In such a case, the baby looks chubby after birth but will eventually lose weight. If your baby loses more than 10% of his weight, it might be a matter of concern, and you should consult the doctor. The doctor will look at factors like feeding and excretion to understand why this is happening.
There is no weight loss after the fifth day of birth. Ideally, babies take 14 days to return to their birth weight, but some might take more time. After this, babies start gaining weight. They gain around 112-200 grams every week, and this continues until they turn four months old. The weight gain in premature babies is usually lesser. Tiny infants gain as low as five grams daily, which goes up to 20 grams daily for large preemies.
How to Calculate the Age of a Premature Baby?
To find out if your premature baby’s weight is average, you need to find the age of your premature baby. The actual age will be different from his date of delivery since he was born prematurely.
Subtract the number of weeks he is premature from the present week (6). This means if your baby is nine weeks old and arrived two weeks earlier, you will need to check whether he is reaching the milestones meant for a seven-week-old rather than a nine-week-old.
Premature Baby Weight Chart
| Gestational Age (weeks) | Average Weight (grams) | Average Weight (ounces) | Average Length (centimetres) | Average Length (inches) | Average Head Circumference (centimetres) | Average Head Circumference (inches) |
| 23 | 584 | 20.6 | 29.9 | 11.8 | 20.9 | 8.2 |
| 24 | 651 | 23 | 31.1 | 12.2 | 21.8 | 8.6 |
| 25 | 737 | 26 | 32.3 | 12.7 | 22.7 | 8.9 |
| 26 | 827 | 29.2 | 33.6 | 13.2 | 23.6 | 9.3 |
| 27 | 936 | 33 | 35 | 13.8 | 24.5 | 9.6 |
| 28 | 1061 | 37.4 | 36.5 | 14.4 | 25.5 | 10 |
| 29 | 1204 | 42.5 | 38 | 15 | 26.5 | 10.4 |
| 30 | 1373 | 48.4 | 39.5 | 15.6 | 27.5 | 10.8 |
| 31 | 1546 | 54.5 | 41 | 16.1 | 28.4 | 11.2 |
| 32 | 1731 | 61.1 | 42.3 | 16.7 | 29.3 | 11.5 |
| 33 | 1956 | 69 | 43.7 | 17.2 | 30.2 | 11.9 |
| 34 | 2187 | 77.1 | 45 | 17.7 | 31.1 | 12.2 |
| 35 | 2413 | 85.1 | 46.2 | 18.2 | 31.9 | 12.6 |
| 36 | 2664 | 94 | 47.4 | 18.7 | 32.7 | 12.9 |
| 37 | 2937 | 103.6 | 48.5 | 19.1 | 33.3 | 13.1 |
| 38 | 3173 | 111.9 | 49.5 | 19.5 | 33.7 | 13.3 |
| 39 | 3338 | 117.7 | 50.2 | 19.8 | 34 | 13.4 |
| 40 | 3454 | 121.8 | 50.8 | 20 | 34.3 | 13.5 |
| 41 | 3530 | 124.5 | 51.3 | 20.2 | 34.5 | 13.6 |
Please note: The measurements given here are averages, and healthy babies may be larger or smaller.
When Do Premature Babies Begin to Gain Weight?
“How to make a premature baby gain weight fast?” Many parents ask their paediatricians this question. The weight gain of preemies depends on many factors. One of the most important is when the baby is born. They start gaining weight a few days after their birth.
Nourishing Your Premature Baby
Breastfeeding is one of the most important things you can do to promote healthy weight gain in your baby. Mother’s milk is the best way to build a premature baby’s strength and health. It will also help prevent all kinds of infections (4).
Colostrum is the first milk your breasts produce, and this is where your baby’s feeding should start. Colostrum is full of nutrients, and it offers all the nourishment that your baby needs at this time (12).
Preemies need to be fed according to a schedule, not on demand. Keep track of when you feed your baby, and try to feed him at regular intervals. This will help your baby get vital nutrients at the right time. Talk to your doctor about how often you need to feed your baby. Your doctor might ask you to feed your baby every two to three hours, and you need to do that even at the cost of your baby’s sleep (1).
When your baby turns four to five months old, the doctor will tell you when and how to introduce solid foods.
How to Feed Your Preemie in the Initial Weeks?
A neonatal paediatrician will analyse your baby’s condition and decide the best way to feed him during the initial weeks. Some of how preemies are fed are:
1. Feeding With IV (Intravenous Lines)
The nutrients and fluids are sent via an IV line into the preemie’s leg, arm, or head (2). This is the preferred method if the baby is very premature, has breathing problems, has not fully developed lungs, or has a premature digestive system.
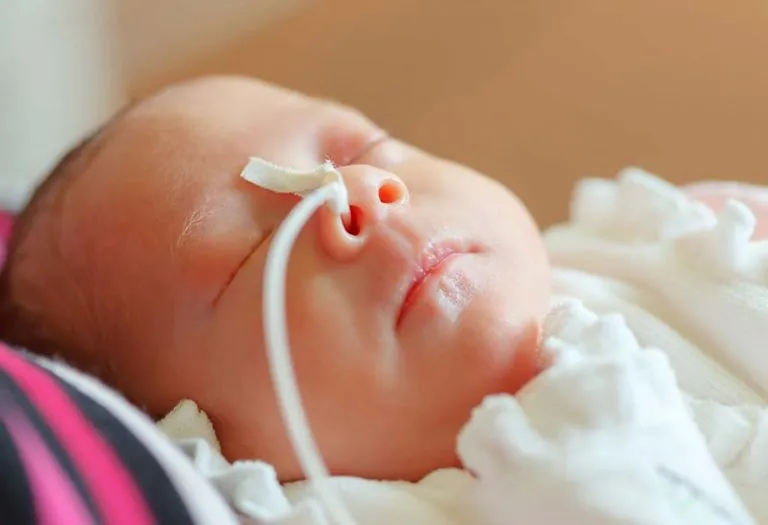
2. Oral and Nasal Feeding
Nasal feeding or gavage feeding involves sending the mother’s milk or formula directly to the baby’s stomach via a tube through the nose or mouth. It is suggested for babies with weak hearts or lungs and coordination problems.
3. Umbilical Catheter
This is a painless way to feed your baby, where the doctor places a tube inside your baby’s umbilical cord (13). Chances of infection are high, so this is recommended only in the most critical cases.
4. Feeding Through Breast and Bottle
When the baby can suck and swallow, the medical team will help you attempt breastfeeding (9).
5. Central Line Feeding
An IV line is inserted in your baby’s vein, and this line delivers the required nutrients to your baby.
6. Fortified Breast Milk or Formula
In some cases, premature infants may require additional calories and nutrients to support their growth and development. Your doctor may recommend supplementing breast milk with a special fortifier or providing formula to boost calorie intake (11).
Baby Tending Tips to Help Your Infant Thrive
- Skin-to-skin contact is essential, as this helps babies gain weight, keeps them warm, regulates their heartbeat and breathing rate, ensures proper sleep, and increases the chances of breastfeeding (8).
- Massaging can also help your baby gain weight (10).
- Ensure you attend even a doctor’s appointment, as checking your baby’s weight regularly is critical.
- Cuddle your baby, give him attention, and keep him happy.
FAQs
1. What is considered the average weight gain for a premature baby?
Premature babies typically have a different growth trajectory compared to full-term infants. On average, premature babies may gain around 15-30 grams (0.5-1 ounce) daily during their initial weeks in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).
2. How can I tell if my premature baby is gaining enough weight?
Monitoring your premature baby’s weight gain is essential for assessing their growth and development. Your doctor will regularly measure your baby’s weight, length, and head circumference to track their progress. Additionally, paying attention to your baby’s feeding patterns, diaper output, and overall demeanour can provide valuable clues about their nutritional intake and well-being.
3. Should I be concerned if my premature baby isn’t gaining weight as quickly as expected?
While premature babies may initially gain weight at a slower pace than full-term infants, persistent weight gain issues could signal underlying health concerns that need to be addressed. Factors such as inadequate calorie intake, feeding difficulties, medical conditions, or developmental issues could contribute to slow weight gain in preemies.
Premature babies are fragile and require care in a controlled environment. The good news is that their chances of survival are high, and weight gain further increases them. The above tips will help you ensure weight gain for your preemie.
References/Resources:
1. Caring for a Premature Baby: Feeding; UnityPoint Health; https://www.unitypoint.org/news-and-articles/caring-for-a-premature-baby-feeding
2. Feeding your premature baby in hospital; Tommy’s; https://www.tommys.org/pregnancy-information/premature-birth/feeding-your-premature-baby-in-the-hospital
3. Low Birth Weight; University of Rochester Medical Center; https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=90&contentid=p02382
4. Breastfeeding your premature baby; NHS; https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/baby/breastfeeding-and-bottle-feeding/breastfeeding/premature-baby/
5. Caring for a Premature Baby: What Parents Need to Know; American Academy of Pediatrics; https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/baby/preemie/Pages/Caring-For-A-Premature-Baby.aspx
6. Your Preemie’s Growth & Developmental Milestones; American Academy of Pediatrics; https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/baby/preemie/Pages/Preemie-Milestones.aspx
7. Preemie; American Academy of Pediatrics; https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/baby/preemie/Pages/default.aspx
8. Skin-to-Skin Contact: How Kangaroo Care Benefits Your Baby; American Academy of Pediatrics; https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/baby/preemie/Pages/About-Skin-to-Skin-Care.aspx
9. 5 Ways to Help Your Premature Baby Thrive; Academy Park Pediatrics; https://www.academyparkpeds.com/post/5-ways-to-help-your-premature-baby-thrive
10. Abraeile. M, Rasooly. A. S, Farshi. M. R, Malakouti. J; Effect of olive oil massage on weight gain in preterm infants: A randomized controlled clinical trial; The Nigerian Medical journal; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4924397/
11. Feeding your premature baby at home; Tommy’s; https://www.tommys.org/pregnancy-information/premature-birth/taking-your-baby-home/feeding-your-premature-baby-home
12. Providing Breast Milk for Premature and Ill Newborns; American Academy of Pediatrics; https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/baby/breastfeeding/Pages/Providing-Breastmilk-for-Premature-and-Ill-Newborns.aspx
13. D’Andrea. V, Prontera. G, Rubortone. S. A, Pezza. L, et al.; Umbilical Venous Catheter Update: A Narrative Review Including Ultrasound and Training; Frontiers in Pediatrics; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8841780/
Also Read:
Preterm Labour and Birth
Premature Baby Health Problems
Premature Babies Development Concerns
Was This Article Helpful?
Parenting is a huge responsibility, for you as a caregiver, but also for us as a parenting content platform. We understand that and take our responsibility of creating credible content seriously. FirstCry Parenting articles are written and published only after extensive research using factually sound references to deliver quality content that is accurate, validated by experts, and completely reliable. To understand how we go about creating content that is credible, read our editorial policy here.





















.svg)


















