W-Sitting Position in Babies and Toddlers – Is It Bad for Your Child?

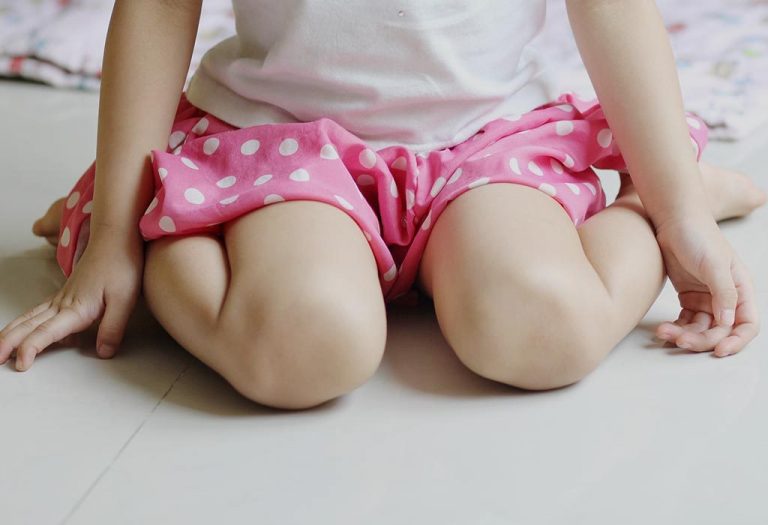
You might have seen your child sit in a ‘W’ position once he begins to hold his body straight without any support. W position sitting is where your child’s legs are stretched outwards, knees bent, and hips turned in. Many parents often wonder if W-sitting is bad for babies and if it requires any intervention. Truth be told, this sitting position is far from ideal and needs correction as soon as possible. If your little one continues to sit in a W sitting pose, it could lead to issues with physical development in the child, which may not be corrected if it is too late.
What Is the W-Sitting Position?
Many children prefer to sit on their hips and bend their knees, spreading their legs outward. When looked from above, the legs and hips seem to form the letter “W”, which gives this position its name (1).
At What Age Does a Child Usually Start to Sit in a W-Position?
Most children adopt this position once they can hold their body upright without any external support. According to the International Hip Dysplasia Institute, children often start sitting position around the age of 3 (2). In toddlers, it is easily found in children around the age of 8-9 (3). Some children correct their style on their own, while others usually continue to sit in the same position while playing or relaxing, especially if they already lack core strength.
Why Do Infants and Toddlers Tend to Sit in This Position?
The W-sitting position is one of the easiest and most comfortable positions since it barely needs any kind of muscle strength and can allow easy access to any direction around the body. Another reason children tend to sit in this position is anatomical. You’ll find this sitting position common in children who have their femurs slightly turned in (femoral anteversion), which makes the ‘W’ sitting position easy (4). This comfort, however, comes at a cost of reduced physical development of the body’s muscles.
Why the W-Sitting Position Should Be Discouraged
There is a strong reason why a toddler sitting in a W-shape needs to be advised to sit properly. The entire position keeps the weight focused, via the trunk, on a singular spot of the body, barely allowing any necessity or freedom of using the upper portion. Apart from that, there are a few disadvantages that arise from sitting in such a pattern all the time.
- The thigh muscles remain tightened throughout this position. When this remains present for a long duration, it can also affect the joints that hold them together, affecting the way your child walk, as well as his gait. It could also lead to tightness in the ips muscles, knees, and ankles (5).
- Since the thigh muscles are not free to relax due to their flexed nature, legs can develop stiffness even in the usual stage, which can be uncomfortable for the child.
- The core section of the child’s body doesn’t receive enough stress, which makes it weak during development. Such a core can result in an unstable movement when the child walks, as well as affect his posture while running or doing various activities.
- The pattern in which the child sits keeps the upper portion of the body fixed in a specific position. The early years are necessary for the body to undergo as many movements and stresses as possible, to develop each area properly. This W-sitting position barely allows any stress on the back as well, making it weak.
- One of the major problems of this sitting position is the distribution of weight. There is barely any, and a majority of it lands on to the hips. Such focused weight pressure can cause dislocation issues in the hips.
Despite several myths, it is to be noted that ‘W’ sitting position is not associated with developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDR) and there is no scientific record of this sitting position leading to hip dislocations or contractures (6) (7).
How to Stop Your Child from Sitting in the W-Position?
Your child might find the W-position quite comfortable to sit in, but it is necessary to stop him from getting used to it. There are ways to help correct that habit as well as ensure that his muscle groups keep developing in strength over time.
- Physical movement is absolutely paramount in ensuring that the physical development of the child continues on the right path at this age. Therefore, encouraging your little one to engage in activities such as swimming, cycling or outdoor games with other kids can help his body get all the movement it needs.
- For young kids who have been sitting in the W-position all this while, massages can help build up the missing strength in the specific muscular regions. These are primarily meant to strengthen the back and other joints of the body.
- The strength of the core and the flexibility of the body is highly impacted by sitting in the W-position. This can be fixed by undertaking yoga exercises. Being accompanied by a proper trainer can truly work wonders.
- Grown-up children could still be used to sitting in the W-position and unaware of the effects it has on their body. Their posture might already be impacted and their back would be weak. It is important to get paediatric advice in knowing how to make corrections for the same.
- It is important to begin correcting your child as soon as you can. Keep reminding him to correct his position, even if it means telling him multiple times in a single day. Breaking a habit will take time.
- If it is difficult for your child to sit in any other position, you can make use of a stool or a chair instead and make it mandatory to sit on it, instead of on the floor.
When to Worry About W-Sitting in Children?
At times, children who keep sitting in the W-position for a major part of their childhood do end up developing certain conditions that affect their gait or physical arrangement. Your child may begin to limp or have a pigeon-toed walking style. These can further result in a loss of muscle strength and clumsiness during movement.
Alternative Sitting Options for Children Who Sit in W-Position
Children who are used to sitting in the W-position cannot be corrected by simply advising them not to do so. It is important to provide them with alternatives that allow them to sit comfortably and get used to the new position.
- Changing their sitting position all of a sudden may not be easy for kids. Therefore, you can start off by giving them a small stool that allows them to stay close to the ground, and engage with other kids or toys while playing.
- Another position is squatting. While this might be difficult for adults, it is quite easy for children since their muscular strength is on the rise. It also helps develop core strength as well as strong legs easily.
- Kneeling can be a better alternative to the W-sitting position. By sliding one foot under the other and resting on that fold, your child can still find it easy to sit on the ground as well as keep the body active.
- At times, the previous kneeling position can gradually return to a W-position unbeknownst to the child himself. Therefore, make use of a half kneel where your child folds one leg but keeps the other as is.
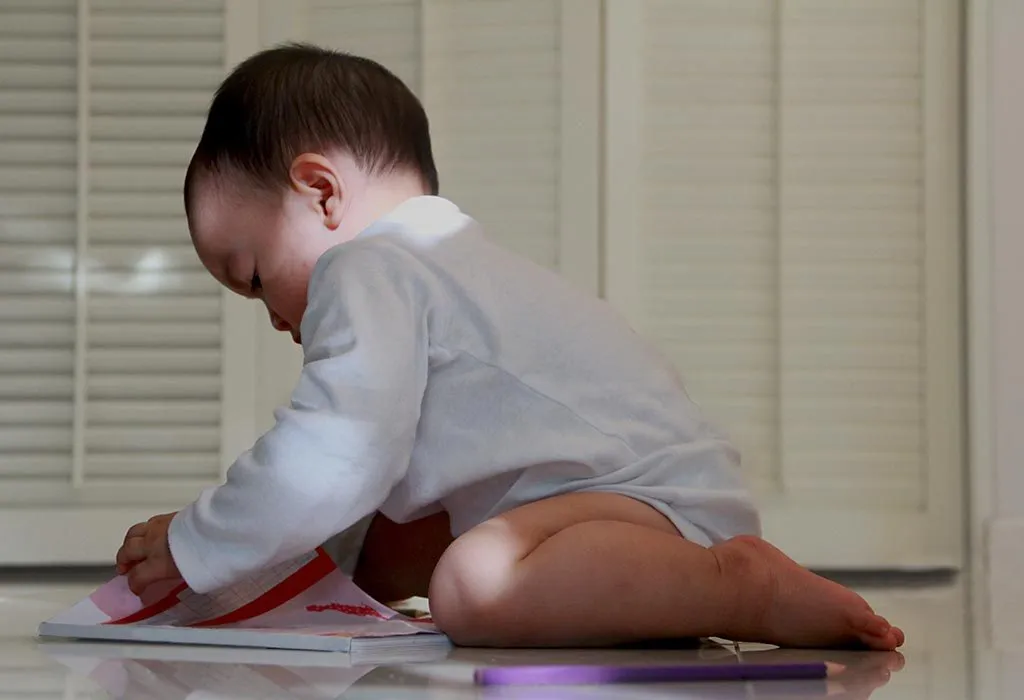
- A quick correction of the W-sitting position can be attained by stretching the legs out front. Make sure your child sits like this when he is reading a book or engaged in a solitary activity.
- While other positions might seem uncomfortable, a side-sitting one can keep the weight partially on the hip as well as on the legs. This helps with an easy transition.
- Gradually, you can ask your child to sit with crossed legs when on the ground. This is the most common position and is safe for the body, too.
FAQs
1. Is W sitting position bad for children?
Children are constantly moving, walking, and trying out different sitting positions. If they sit in the W sitting position once in a while, then it is not harmful. However, sitting in this position is neither ideal nor safe for children as I will cause movement and posture problems in the later stages of their life (5).
2. Does the W sitting position require parents’ intervention, or can it only be treated with paediatric physical therapy?
The W sitting pose can be changed by the intervention of both parents and paediatric physical therapy. As parents, you can keep an eye on your child’s sitting position, and whenever you see a compromised position, you can change it. You can gradually demonstrate to your little one how to sit and stand at home only. Paediatric physical therapy also works great as it is done under an expert’s guidance.
3. What are the possible complications of sitting in the W pose?
A 2015 research done on healthy infants w-sitting on a daily basis, it was found that If a child keeps on sitting in the W sitting pose on a daily basis, they are likely to develop orthopaedic diseases, back pain, or even damage to the anterior cruciate ligament (8).
Correcting W-sitting in babies and toddlers is the best way to nip the origin of the habit. Your children’s early years play a key role in their development, and it is necessary to make sure they progress in the best way possible.
References/Resources:
1. Gonzales. J; Why W-sitting might be a cause for concern; Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children; https://www.arnoldpalmerhospital.com/content-hub/why-w-sitting-might-be-a-cause-for-concern
2. W-Sitting and Hip Development; International Hip Dysplasia Institute; https://hipdysplasia.org/w-sitting-and-hip-development/
3. Rachwani. J, Soska. K. C, Adolph. K. E; Behavioral flexibility in learning to sit; Dev Psychobiol. 2017 Dec;59(8):937-948. doi: 10.1002/dev.21571. Epub;PubMed; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5690822/; October 2017
4. Park. Y, Byun. H, Kim. M. J, Shin. H; Change of Femoral Anteversion Angle in Children With Intoeing Gait Measured by Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography Reconstruction: 3-Year Follow-Up Study; Ann Rehabil Med.; PubMed Central; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10326397/; June 2023
5. What is W-Sitting?; Pathways.org; https://pathways.org/what-is-w-sitting/
6. Rethlefsen SA, Mueske NM, Nazareth A, Abousamra O, Wren TAL, Kay RM, Goldstein RY. Hip Dysplasia Is Not More Common in W-Sitters; Clin Pediatr (Phila).; PubMed; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32659120/; October 2020
7. Honig. E. L, Haeberle. H. S, et al.; Pediatric orthopedic mythbusters: the truth about flexible flatfeet, tibial and femoral torsion, W-sitting, and idiopathic toe-walking; Curr Opin Pediatr.; PubMed; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33315688/; February 2021
8. Fujimori. M, Natuzako. A, Tsurusaki. T; Effect of W-sitting on Standing Posture of Preschool Age Children; Rigakuryoho Kagaku, Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 429-432; J-stage; https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/rika/30/3/30_429/_article; 2015
Also Read:
Bowed Legs in Babies
How to Help a Baby Sit Up on His Own?
Baby Sleeping Position – What Is Safe?
Hypertonia or Stiff Limbs in Toddlers
Was This Article Helpful?
Parenting is a huge responsibility, for you as a caregiver, but also for us as a parenting content platform. We understand that and take our responsibility of creating credible content seriously. FirstCry Parenting articles are written and published only after extensive research using factually sound references to deliver quality content that is accurate, validated by experts, and completely reliable. To understand how we go about creating content that is credible, read our editorial policy here.



















.svg)


















