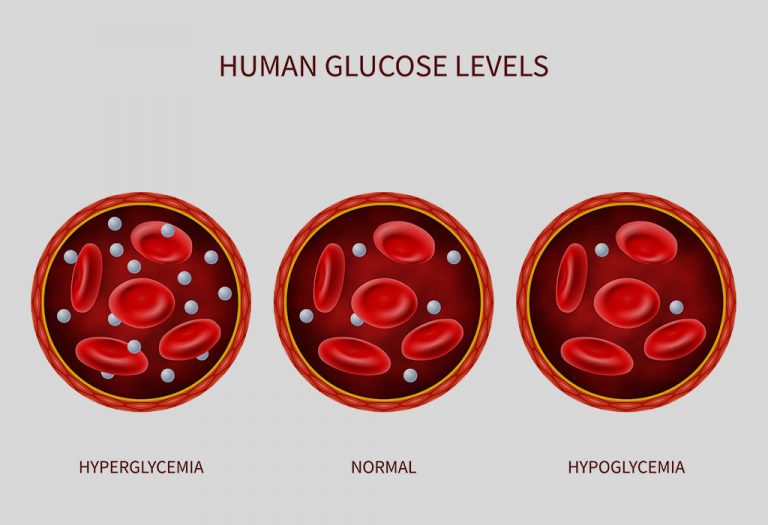
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia) in Pregnancy

The food that we consume is broken down into sugar that is glucose. Glucose then enters the various cells of the body and provides energy for metabolic processes that keep the body running. If there is not enough glucose in the blood, it can lead to a condition known as ‘hypoglycemia’ or low blood sugar, which means the concentration of dissolved sugar in the body is below the required amounts. This can cause mild to severe complications depending on the extent of hypoglycemia.
In simple cases, it can cause lethargy and tiredness, but if it is in the advanced state, it may lead to fainting or even coma. Being hypoglycemic is problematic in itself, but if it happens during pregnancy, you will have to take extreme care to control it. Read this article to know the causes that lead to low blood sugar in pregnancy and how it affects pregnancy.
What Is Hypoglycemia in Pregnancy?
Hypoglycemia occurs when the normal blood sugar range falls below 700 micrograms per millilitre in pregnancy. In contrast, the normal range for blood sugar should be between 700 and 1000 micrograms per millilitre (1).
Types of Hypoglycemia
If you observe any symptoms of hypoglycemia, please contact your doctor as soon as possible so you can be diagnosed and treated well in time. There are two common types of hypoglycemia that occur during pregnancy. They are as follows (2):
1. Reactive Hypoglycemia
In reactive hypoglycemia and pregnancy, the levels of blood sugar tend to fall rapidly within the first couple of hours after you have had a meal. This type of hypoglycemia is more common in diabetics but is also observed in people without the condition.
2. Fasting Hypoglycemia
In fasting hypoglycemia, the blood sugar falls to dangerous levels in between your meals. This type is more common in people without diabetes.
Who Is More Prone to Hypoglycemia?
Pregnant women who are most prone to hypoglycemia in the following conditions:
- A pregnant woman is more prone to hypoglycemia during the end of the first trimester, especially between 8 and 16 weeks of pregnancy.
- If you frequently fall sick during pregnancy, it can lead to hypoglycemia.
- A history of low blood sugar or hypoglycemic attacks can also lead to hypoglycemia.
What Causes Low Blood Sugar in Pregnancy?
There are several potential causes of hypoglycemia in pregnancy. Some of them include (3):
1. Morning Sickness
Morning sickness or nausea and vomiting during pregnancy can cause low blood sugar. This is because you might be rejecting more food than you are consuming, leading to a caloric deficit in your daily diet. If you find that you are vomiting frequently, losing weight, and feeling faint or dizzy, please contact your doctor for advice.
2. Lifestyle
There are various lifestyle factors that affect blood sugar levels in the body. For instance, overexercising leads to excess glucose being broken down for the energy burst required. Another factor is not consuming enough food, that is less than 1800, 2200 and 2400 calories per day in the first, second and third trimester, respectively. Consuming alcohol can also lead to hypoglycemia as it impedes with the release of blood sugar from the liver.
3. Diabetes
Hyperglycemia, or raised levels of blood sugar, is common during pregnancy. This is the result of diabetes, in which the hormone insulin does not efficiently transport blood sugar to the cells, leading to excess sugar in the bloodstream. However, hypoglycemia can occur because of diabetes medications, such as insulin injections. These insulin injections can lower the blood sugar levels in the body more than required, leading to hypoglycemia. In other cases, hormonal changes in your pregnancy can lead to hypoglycemia in women who have diabetes, even if they are not taking insulin medication. Please ensure that you consume well-balanced meals during your pregnancy as well as keep an eye on your blood sugar levels if you are pregnant and diabetic.
4. Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a pregnancy condition, which is caused due to hormonal effects, pregnancy stress, and resistance to insulin. Your blood sugar levels can drop due to these causes and lead to hypoglycemia. Gestational diabetes is especially likely in women who have diabetes and are on medication. Approximately 9% of women suffer from gestational diabetes during their pregnancy, but the condition resolves on its own after giving birth.
5. Medical Conditions
Several medical problems can lead to hypoglycemia in pregnancy without diabetes. As some of them might cause complications in your pregnancy and in foetal development, it is important to obtain proper treatment. These disorders include glucagon and cortisol hormone imbalances, acute hepatitis, organ failure, enzyme deficiencies, pancreatic tumours, and so on.
6. Medication
In addition to insulin, other diabetes medications can lower blood sugar levels. Oral medicines like sulfonylureas and meglitinides are used to treat diabetes and can cause hypoglycemia. Several other medicines are also used in reducing blood sugar levels, such as sulfonamides, pentamidine, quinine, and salicylates.
But, how does one know they have hypoglycemia during pregnancy? Read on for some signs and symptoms you need to look out for.
Signs and Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar During Pregnancy
As sugar is the source of energy for many of the body’s metabolic processes, low blood sugar will cause several symptoms to manifest. Some of them include (4):
- Weakness, tiredness, and fatigue can make you exhausted and cranky.
- It becomes harder to think with clarity.
- The body begins to sweat and shake uncontrollably often.
- You might experience irregularity or an increase in your heart rate.
- Your vision might become blurry and unclear.
- You may experience fluctuations in mood and anxiety levels.
- If your hypoglycemia is severe, you might suffer from convulsions and seizures, and even lose consciousness.
- Hypoglycemia symptoms can also show up during sleep; therefore watch out for these signs, too –
- Cold night sweats
- Frequent nightmares
- Tired even after a good night’s sleep
- Difficulty in waking up in the morning
Diagnosis of Low Blood Sugar in Pregnant Women
Gestational diabetes is usually tested during the second trimester, but if women show symptoms of diabetes, more tests might be required. If you do not have diabetes, your doctor might suggest more blood tests to identify the cause of your hypoglycemia. Further, the doctor might require you to furnish detailed descriptions about your medical history, diet, exercise routine, and so on.
Effects of Hypoglycemia on Pregnancy
Hypoglycemia can have an effect on both the mother and the baby during pregnancy.
1. Effect on the Mother
Severe cases of hypoglycemia might require hospitalisation. Further, gestational diabetes is known to result in complicated labours, leading to potential injuries while giving birth. Hypoglycemic attacks can occur at night during early pregnancy, where the blood sugar level can drop to 300 micrograms per millilitre. This can result in seizures and in extreme cases, a coma.
2. Effect on Baby
Low blood sugar during pregnancy can also affect the health of the baby – foetal development, such as physical and mental abnormalities, low birth weight and so on. Pregnant women with gestational diabetes have an increased risk of giving birth to babies with jaundice. These babies often have drastically low blood sugar levels and need careful monitoring.
Treatment of Hypoglycemia in Pregnancy
If the case of hypoglycemia is severe, there are a few treatment methods which can be employed:
- Feeding the patient high-calorie foods such as fruit juice, sugar water, glucose tablet can help. In total, there should be approximately fifteen grams of carbohydrates. The blood sugar should normalise within fifteen minutes of eating the carbs.
- In case the patient cannot eat or drink, visit a doctor at the earliest.
- During labour and delivery, it is vital to monitor blood sugar levels.
- In rare cases, tumours causing hormonal imbalance will need to be removed during the pregnancy.
Precautions to Take While Suffering from Hypoglycemia During Pregnancy
Pregnant women with hypoglycemia can take a few precautions to regulate the condition (5):
- Avoid alcohol at all costs.
- Check your blood sugar levels with a portable glucometer.
- Keep a sugary snack handy at all times.
- Eat frequent smaller meals, rather than three large meals a day.
- If you are working out more on a particular day, consume more food.
- If you have been prescribed insulin, remember to take the right doses at the right time.
When to Consult the Doctor
While mild episodes of low blood sugar can often be managed with dietary adjustments, certain situations require immediate medical attention to ensure the health and safety of both mother and child.
- If you experience recurrent episodes of low blood sugar despite eating regular meals, it’s important to consult your doctor to rule out underlying conditions like gestational diabetes or other metabolic issues.
- Seek medical help if you experience severe symptoms such as confusion, fainting, seizures, or inability to eat or drink, as these could indicate dangerously low blood sugar levels.
- If your blood sugar levels do not stabilize after consuming fast-acting carbohydrates (like juice or glucose tablets), contact your healthcare provider immediately.
- If hypoglycemia is interfering with your daily activities or causing significant anxiety, your doctor can help adjust your management plan or investigate further.
FAQs
1. Is hypoglycemia in pregnancy linked to postpartum health issues?
In some cases, recurrent hypoglycemia during pregnancy may indicate an underlying metabolic issue that could persist postpartum. Consulting your doctor can help identify and address any long-term concerns.
2. Can hypoglycemia in pregnancy trigger neurological symptoms like tingling or numbness?
While rare, some women may experience tingling, numbness, or even temporary vision changes during a hypoglycemic episode. These symptoms occur due to the brain’s response to low glucose levels and should be reported to your healthcare provider immediately.
3. Does hypoglycemia during pregnancy increase the risk of sleep disturbances or nightmares?
Low blood sugar at night can disrupt sleep patterns and even cause vivid dreams or nightmares. If you wake up frequently feeling shaky, sweaty, or confused, it could be a sign of nocturnal hypoglycemia, which requires medical attention.
This was all about hypoglycemia and pregnancy. Hypoglycemia can occur during your pregnancy for various reasons, even if it’s skipping a single meal. If you notice any symptoms of hypoglycemia as described in this article, please consult with your doctor so he/she can accurately diagnose and prescribe treatment for the condition. You can also check with your doctor if you need to know how to lower blood sugar during pregnancy in case you have hyperglycemia.
References/Resources:
2. Cleveland Clinic – Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
3. Cincinnati College of Medicine – About High and Low Blood Sugar
4. NHS – Low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia)
5. CDC- Treatment of Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
Also Read:
Low BP in Pregnancy
High BP in Pregnancy
Insulin during Pregnancy
Progesterone Levels During Pregnancy
Was This Article Helpful?
Parenting is a huge responsibility, for you as a caregiver, but also for us as a parenting content platform. We understand that and take our responsibility of creating credible content seriously. FirstCry Parenting articles are written and published only after extensive research using factually sound references to deliver quality content that is accurate, validated by experts, and completely reliable. To understand how we go about creating content that is credible, read our editorial policy here.