14 Fun and Interesting Polar Bear Facts for Kids
- What Is a Polar Bear?
- Where Do They Live?
- Types of Polar Bears
- What Do They Eat?
- What Is the Behaviour of a Polar Bear Like?
- How Do Polar Bears Adapt to Their Environment?
- Other Interesting and Fun Facts About Polar Bears for Kids
- FAQs
Polar bears are some of the most beautiful animals on Earth, enchanting children and adults. These majestic animals, often seen roaming the icy landscapes of the Arctic, have an almost magical presence. But did you know that polar bears have some pretty amazing traits and habits that make them stand out in the animal kingdom? Learning about polar bears can be a thrilling adventure filled with wonder and excitement for kids. Here, we will discuss some fun and exciting polar bear facts for kids that will entertain and educate young minds. Let’s embark on this chilly adventure together and uncover the amazing world of polar bears!
What Is a Polar Bear?
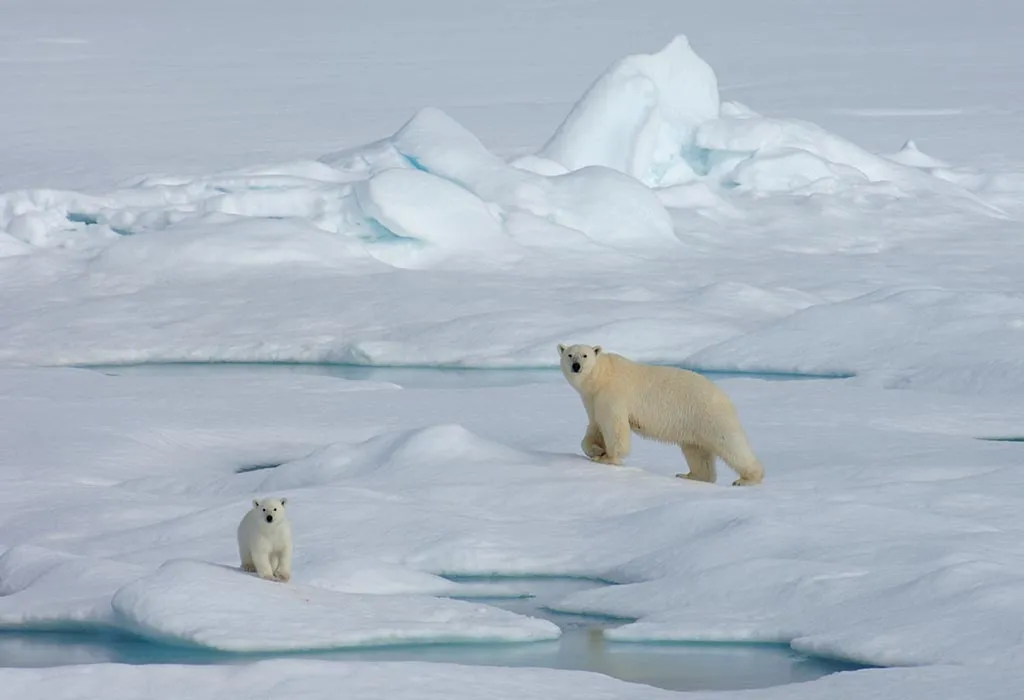
Polar bears are large, powerful predators that thrive in the icy wilderness of the Arctic. Known for their striking white fur and impressive size, they are the largest land carnivores on Earth. They are perfectly adapted to life in the extreme cold, making them one of the most fascinating animals for children to learn about.
Where Do They Live?
Polar bears are mainly found in the Arctic, thriving in one of the harshest environments on the planet. In this icy wilderness, they hunt, play, and raise their young, perfectly adapted to the cold and ice. Here are six locations where these animals are found.
1. Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is the primary region where polar bears live. This vast area includes parts of Canada, Greenland, Norway, Russia, and the United States (Alaska). It is characterised by extreme cold, sea ice, and long winters.
2. Canada
Canada is home to about 60% of the world’s polar bears. Polar bears are particularly common in northern regions, such as Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, and Manitoba. Churchill, Manitoba, is famously known as the “Polar Bear Capital of the World.”
3. Greenland
Greenland, the world’s largest island, is another habitat for polar bears. The coastal areas, especially along the northern and eastern coasts, provide an ideal environment for hunting seals and raising cubs.
4. Norway (Svalbard)
The Svalbard archipelago, located in the Arctic Ocean, is part of Norway and is home to a significant polar bear population. These bears roam the sea ice and islands and are often spotted by tourists who visit the region.
5. Russia
In Russia, polar bears are mostly found along the Chukchi and East Siberian Seas. These remote areas provide the isolation and access to sea ice that polar bears need for hunting and survival.
6. United States (Alaska)
Polar bears are commonly found along Alaska’s northern coast and on the Beaufort and Chukchi Seas sea ice. This region offers the cold climate and frozen waters that polar bears require to thrive.
Types of Polar Bears
While polar bears might all look similar with their snowy white coats, they have subtle differences depending on their location. These variations have led scientists to identify distinct populations rather than separate species. Here are the types of polar bears based on their location.
1. Polar Bears in the Western Hudson Bay
Polar bears living in Canada’s Western Hudson Bay area are one of the most studied populations. These bears are commonly seen along the shores when the sea ice melts during summer. Due to the shorter hunting season, they tend to be slightly smaller than those found in other regions.
2. Polar Bears in the Chukchi Sea
Polar bears in the Chukchi Sea, located between Alaska and Russia, are known for their resilience in an environment where sea ice is rapidly changing. This population is adapted to living with thinner, less stable ice and has been observed to travel great distances in search of food.
What Do They Eat?
Polar bears are carnivores, meaning their diet primarily consists of meat. However, due to the harsh conditions of the Arctic, their food sources are limited, and they have become specialised hunters. Below is a list of what polar bears eat to survive in their icy habitat.
1. Seals
Seals are polar bears’ main prey, with ringed and bearded seals being the most common targets. Polar bears rely heavily on seal fat to maintain energy levels, especially during the harsh winter.
2. Walruses
Though less common, polar bears may also hunt walruses, particularly younger or weaker individuals. Walruses are much larger and more dangerous prey, so polar bears usually avoid them unless other food sources are scarce.
3. Fish and Marine Mammals
Occasionally, polar bears will eat fish or scavenge on the remains of other marine mammals, such as whales. These are not their primary food sources but can be important when seals are scarce.
4. Birds and Eggs
During the summer, when sea ice retreats and seals are more challenging to catch, polar bears might turn to birds and their eggs as food sources. This is more of a supplementary diet often seen in younger bears or females with cubs.
5. Vegetation and Berries
Although polar bears are primarily meat-eaters, they have been known to consume some vegetation, such as berries, grasses, and seaweed. This behaviour is more common in areas where food is limited, and it helps them to survive when their preferred prey is unavailable.
What Is the Behaviour of a Polar Bear Like?
Polar bears are fascinating animals whose various behaviours reflect their adaptability to the harsh Arctic environment. Here are a few of their behavioural traits.
1. Solitary Animals
Polar bears are generally solitary animals, spending most of their lives alone. They come together mainly during the breeding season or when a mother raises her cubs.
2. Patient Hunters
Polar bears are patient hunters. They often wait for hours by seal breathing holes in the ice. This technique, known as “still hunting,” is one of their primary methods of catching prey.
3. Excellent Swimmers
Polar bears are excellent swimmers, able of covering long distances in search of food. They have been known to swim for days without rest, using their large paws as paddles and their body fat as insulation against the cold water (5).
4. Seasonal Behaviour
During the winter, polar bears are active hunters, using the extensive sea ice to catch seals.
During the summer, when the ice melts, they may enter a state of “walking hibernation,” in which their metabolism slows to conserve energy.
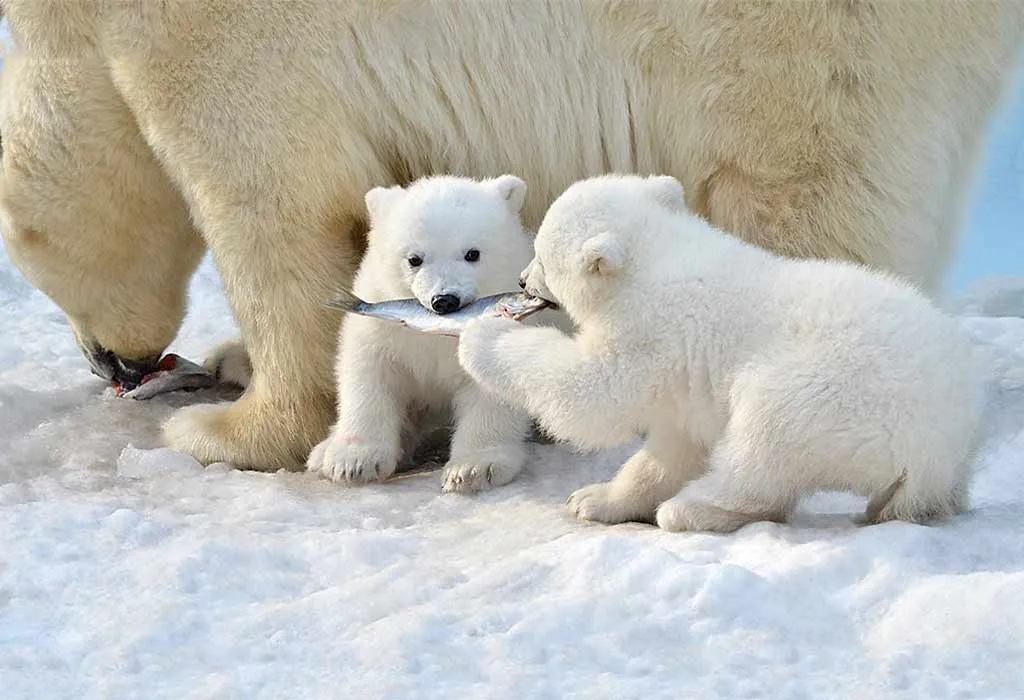
5. Mother-Cub Bonding
Female polar bears are highly protective of their cubs and spend up to two and a half years caring for them. The bond between a mother and her cubs is strong, and the mother teaches the cubs essential survival skills.
6. Playful Nature
Polar bear cubs are playful, engaging in mock fights and wrestling with their siblings. This play behaviour is crucial for developing their hunting skills and social interactions.
7. Territorial Behaviour
While not overly aggressive, polar bears can be territorial, especially males during breeding. They may engage in fights over mates or food, though these encounters are usually more about displays of strength than violence.
8. Denning
Pregnant female polar bears create snow dens where they give birth and protect their young during the harshest winter. These dens provide a warm, safe environment for the cubs to grow until they are ready to face the outside world (2).
9. Scent Marking
Polar bears use scent markings to communicate with other bears. They leave their scent on the ground, ice, or objects in their environment, which helps them establish territories and identify each other.
10. Dietary Adaptations
In food scarcity, polar bears can slow their metabolism to conserve energy. They also eat almost anything available.
11. Curiosity Towards Humans
Polar bears are naturally curious animals and may approach humans or human settlements, especially in areas where their natural prey is scarce. While they generally avoid confrontation, their sheer size and power make them dangerous, so caution is always advised when in polar bear territory.
How Do Polar Bears Adapt to Their Environment?
Polar bears are masters of survival, perfectly adapted to the extreme conditions of the Arctic. Their physical and behavioural traits have evolved over thousands of years, enabling them to thrive in one of the coldest environments on Earth. Let’s look at how polar bears adapt to their environment.
1. Thick Fur Coat
Polar bears have a dense fur coat that provides excellent insulation against the freezing Arctic temperatures. Their fur consists of a dense undercoat and an outer layer of guard hairs, which trap heat close to their bodies.
2. Black Skin
Beneath their white fur, polar bears have black skin, which helps them absorb heat from the sun. This is especially important during the short Arctic summer when sunlight is more abundant.
3. Layer of Blubber
Underneath their skin, polar bears have a thick layer of fat, sometimes up to 11 centimetres thick. This layer of fat insulates the bears and acts as an energy reserve during food scarcity.
4. Large Paws
Polar bears have large, wide paws that help them walk on thin ice and deep snow without sinking. Their paws also act as paddles when swimming, making them powerful and efficient swimmers.
5. Sharp Claws
Polar bears use their sharp claws to hunt and grip the ice. They also use their claws to catch seals, dig through snow, and break the ice to reach their prey.
6. Keen Sense of Smell
Polar bears possess an exceptional sense of smell, allowing them to detect seals from several kilometres away, even beneath thick ice layers.
7. Camouflage
The white colour of their fur provides camouflage against the snow and ice, helping polar bears blend into their environment. This is especially useful for sneaking up on unsuspecting seals during hunts.
8. Seasonal Metabolic Changes
Polar bears can slow their metabolism during food scarcity, such as when sea ice melts in the summer. This adaptation allows them to conserve energy until their preferred prey becomes more accessible.
9. Still Hunting
Polar bears use a hunting technique called “still hunting,” where they wait by seal breathing holes in the ice. This method requires patience and helps them conserve energy while waiting for a seal to surface.
10. Strong Parental Care
Mother polar bears provide extensive care for their cubs, teaching them essential survival skills and guarding them from predators and harsh environmental conditions. This strong bond ensures the cubs’ survival in the challenging Arctic environment.
Other Interesting and Fun Facts About Polar Bears for Kids
Polar bears are full of surprises, with unique characteristics and behaviours that make them truly fascinating. Beyond what we’ve already discussed, here are some more interesting and fun facts about polar bears.
1. Polar bears are the largest land carnivores on the planet, with adult males weighing between 350 and 700 kilograms (2). That’s heavier than a small car!
2. The newborn polar bear cubs are tiny, weigh less than a kilogram, and are blind. In the first few weeks of their lives, they rely entirely on their mother for warmth and protection.
3. While polar bears appear white, their fur is transparent. The hollow structure of each hair reflects and scatters visible light, giving it its white appearance, which helps it camouflage with its snowy environment (4).
4. Despite living in one of the coldest places on Earth, polar bears can overheat due to their thick fur and fat layers. They sometimes stretch out on the ice or swim in cold water to cool down.
5. Polar bears have 42 teeth specially adapted for their carnivorous diet. They use their sharp canines to catch and kill seals and their molars to shear and grind food.
6. Polar bears communicate with each other through various body language signals, such as nose-to-nose greetings, which are a way of asking for food, and a lowered head, which indicates submission (3).
7. Despite their massive size, polar bears are surprisingly fast runners. They can reach up to 40 kilometres per hour, though they prefer to conserve energy and avoid running unless necessary.
8. Polar bears possess an excellent sense of direction, vital in the vast and featureless Arctic landscape. They can navigate large distances of ice and snow, returning to familiar hunting grounds or denning areas.
9. Some scientists believe that polar bears are left-handed, meaning they may prefer using their left paws more frequently when hunting or interacting with their environment.
10. Polar bears have a sense of hearing quite similar to humans, allowing them to detect sounds in their environment, such as the movement of prey under the ice.
11. These bears are powerful and can leap over 1.8 metres out of the water to catch prey or cross gaps in the ice. Their strength and agility are truly impressive for animals of their size.
12. Because they stay mostly on the sea ice of the Arctic Ocean rather than on land, polar bears are categorised as marine animals (1).
13. Polar bears have a transparent third eyelid that acts like built-in sunglasses, protecting their eyes from the intense rays of the Arctic sun and the reflective snow.
14. Polar bears are apex predators essential to the Arctic ecosystem. They help maintain the balance by keeping seal populations in check, which affects the entire food web in their environment.
FAQs
1. How long do polar bears live?
Polar bears typically live for about 20 to 30 years in the wild, with some reaching up to 35 years in ideal conditions.
2. Can polar bears see in the dark?
Yes, polar bears have excellent night vision, which helps them hunt during the long Arctic winters when there is little to no sunlight.
3. In one meal, how much can a polar bear eat?
To build up fat reserves for colder months, a polar bear can eat up to 45 kilograms of food in a single meal, especially after a successful seal hunt.
Polar bears are truly remarkable animals, perfectly adapted to the harsh conditions of the Arctic. Learning about these species can help children better understand wildlife and the value of protecting their natural habitats. Let’s all do our part to ensure these majestic animals thrive for generations.
References/Resources:
1. TOP 10 FACTS ABOUT POLAR BEARS; WWF-UK; https://www.wwf.org.uk/learn/fascinating-facts/polar-bears
2. Nielsen. B; 10 Surprising Facts About Polar Bears; Polar Bears International; https://polarbearsinternational.org/news-media/articles/surprising-facts-about-polar-bears
3. Polar Bear Behavior; Polar Bears International; https://polarbearsinternational.org/polar-bears-changing-arctic/polar-bear-facts/behavior/
4. Why do polar bears have white fur? And nine other polar bear facts; WWF-UK; https://www.worldwildlife.org/stories/why-do-polar-bears-have-white-fur-and-nine-other-polar-bear-facts
5. Polar Bear; National Wildlife Federation; https://www.nwf.org/Educational-Resources/Wildlife-Guide/Mammals/Polar-Bear
Also Read:
Fun Facts About Wolf for Kids
Exciting facts about Animals for Kids
Interesting Penguin Facts for Kids
Was This Article Helpful?
Parenting is a huge responsibility, for you as a caregiver, but also for us as a parenting content platform. We understand that and take our responsibility of creating credible content seriously. FirstCry Parenting articles are written and published only after extensive research using factually sound references to deliver quality content that is accurate, validated by experts, and completely reliable. To understand how we go about creating content that is credible, read our editorial policy here.
















.svg)
















