Cognitive Development in Children – What It Is & Stages

Children grow up in the blink of an eye, right from early childhood to their formative years as teenagers! During that blink of time is when the magic happens. Watching your child grow emotionally as well as mentally, and not just physically, makes you proud as a parent, and creates fond memories. Every milestone they reach—from their first words to their first day of school—shapes their future. Parents play a crucial role in nurturing their child’s learning and curiosity.
Cognitive development in children is a key aspect of their growth. Learn what you can do to enhance cognitive development in preschool children, and find out what the four major stages of cognitive development in kids are.
What Is Cognitive Development?
Here’s the cognitive development meaning. Cognitive development refers to the development of thinking, reasoning, problem-solving, and creative skills (1). A whole-brain cognitive development ensures that your child grows mentally and emotionally. According to famous psychologist Jean Piaget, children are found to be as intelligent as adults, the only difference being in their thought processes.
Contrary to popular belief, children do not soak up information like a sponge and try to make sense of the world around them. Their perceptions and perspectives develop and sharpen as a result of cognitive development.
Why Is Cognitive Development Important in Children?
Cognitive development is crucial in children because it lays the foundation for how they learn, think, reason, and interact with the world. Strong cognitive skills enable children to process information, solve problems, make decisions, and develop critical thinking abilities—all of which are essential for academic success and lifelong learning (2).
Additionally, cognitive development supports:
- Language and communication skills – Helping children express themselves and understand others.
- Memory and concentration – Allowing them to retain information and focus on tasks.
- Logical reasoning – Encouraging them to analyse situations and make sound judgments.
- Creativity and imagination – Fostering innovation and adaptability in learning.
By nurturing cognitive development in early childhood, parents and educators can help children build confidence, independence, and a strong ability to adapt to new challenges. Investing in cognitive growth ensures that children are well-prepared for school, social interactions, and future success in life.
A notable cognitive development example is the emergence of object permanence in infants. This milestone—understanding that objects continue to exist even when out of sight—typically develops between 4 to 7 months of age and signifies a fundamental shift in a child’s cognitive processing.
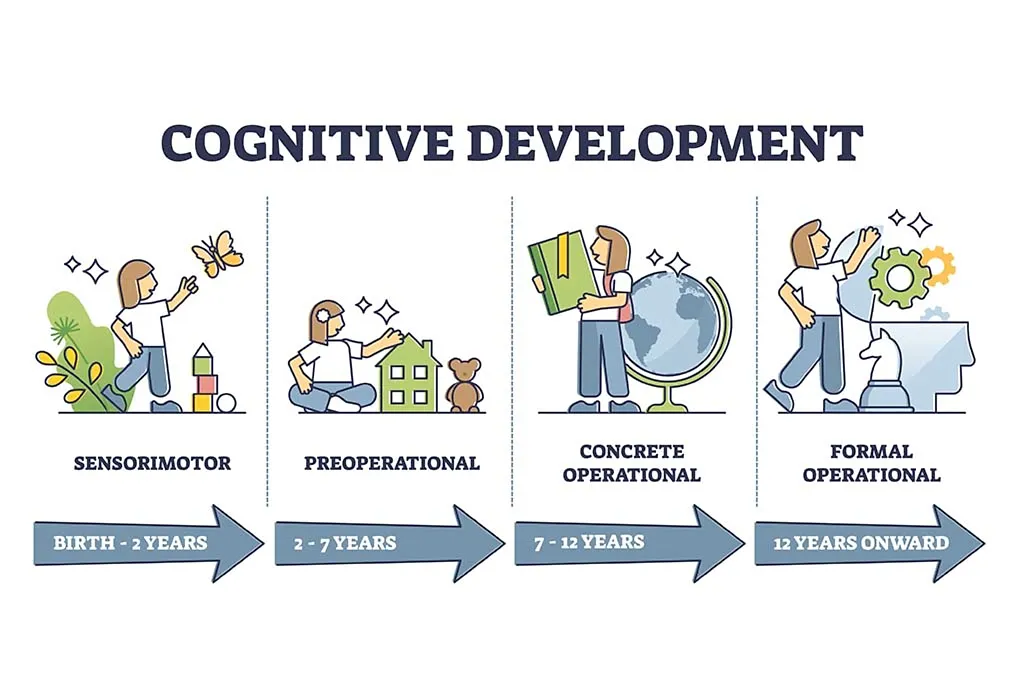
Major Stages of Cognitive Development in Early Childhood
At every stage of your child’s development, several changes take place in terms of cognitive development. When your child enters the world, he goes through the four main stages of cognitive development, which are listed below (3):
1. The Sensorimotor Stage (Birth to 2 Years)
In this stage, children soak in the sensations and perceptions of the world through their motor senses. They gleefully go through life and enjoy their surroundings to the fullest, learning especially through the manipulation of objects and by touch. This is when their senses become activated as they continue to make sense of sensory perceptions and gain awareness of their surroundings.
2. The Preoperational Stage (2 Years to 7 Years)
The period of time between ages two and seven is dubbed as the preoperational Stage. This is the stage when children are not able to make sense of logic but are able to understand images and symbolic representations of information. Put simply, this is when they learn visually, and their memory, imagination, and creativity begin to take shape. Children typically do not understand the viewpoints of others, and this is when they begin picking up basic words of languages.
3. The Concrete Operational Stage (7 Years to 11 Years)
Children begin to gain awareness of their surroundings and perceive others’ feelings between ages of seven and eleven. This is when emotional development takes place, as they begin to be aware of others’ emotions and understand external events. Abstract and hypothetical thinking remains a problem, but the foundations of logical thinking and analysis begin building from this point on.
4. The Formal Operational Stage (12 years and Up)
The period between the ages of twelve and adulthood is referred to as the Formal Operational Stage. This is when kids begin to further develop their logical thinking skills and learn abstract reasoning and concepts. Systematic planning and problem-solving logical issues start to take shape in the brain during these years.
Tips to Develop Cognitive Skills in Kids
There are several ways you can boost your child’s cognitive development. Here are our top ten recommended tips for enhanced cognitive development in early childhood:
1. Sing Songs
Encourage your child to sing along with you. This promotes memory development and creating associations between words and images (4).
2. Noise Identification
Teach your child to identify and distinguish between different sounds throughout the word. Whether it’s a bird singing, water running, or a dishwasher grinding, ask your child to identify noises and relate them to objects or actions pertaining to his daily environment.
3. The Alphabet Game
Cut out alphabet pieces and tape them to different areas of your home. Encourage your child to go alphabet hunting and finding the missing pieces in sequence. Let him collect the shapes and tape them in order while singing along pleasant tunes related to those letters to facilitate word identification and image associations.
4. Shape Practice
Play balls and fun, colourful games with your child which involve manipulating shapes, like building blocks or puzzle pieces (5). As your child slowly grows, ask him/her to talk about objects near them and describe colours and proportions.
5. The Decision Game
Give your child tasty treats and ask him to pick between the different flavours available.
- Would he prefer pizza for dinner, or a burger?
- Would he prefer to go to the park, or play video games at a friend’s place?
- Red sweater or brown overcoat?
By offering your child choices, you’ll make them feel independent and enable freedom of thought and speech, thus facilitating their cognitive development.
6. Asking Questions
Ask your child questions regarding making daily choices. Asking helps your child think, and enables him to become a better problem-solver. It also helps him understand how his surroundings work.
7. Outings and Trips
Take your child outdoors, visit the museum, the amusement park, and so on. Let your child embark on outdoor adventures and have fun. Let him loose in the garden, catch bugs, go insect hunting, and quench his curiosity by asking questions related to outdoor events. Museum trips and taking him grocery shopping are also great ideas.
8. Play Fun Games
From matching lids with pots according to shapes, colours, and container types, to playing jigsaw and board games with kids, playing fun games that facilitate social bonding and logical interactions help build key cognitive skills in areas of their brains. You may even let them play video games once in a while to bring a twist to everyday things! Outdoor games like ‘Peek-a-boo’ and ‘Hide and Seek’ are recommended game suggestions.
9. Count Objects
Teach your child to count objects, vegetables, shoe pairs, and anything simple and fun! By practising counting, he can build his logical thinking skills (6). You can make it even more fun by asking how many chocolates he wants on his birthday or how many places to visit during weekends! Make him count, make him practice names, and he’ll remember!
10. Exercise and Sports
Teach your child a sport and show him how to exercise. Exercises release endorphins and make kids feel good. Plus, it’s beneficial to their health and develops coordination and fine motor skills. Creative exercises like dancing and scavenger hunts outdoors promote logical and creative thinking alongside dexterity and sensory development (7).
FAQs
1. How does bilingualism affect cognitive development in young children?
Bilingualism boosts brain development by improving focus, problem-solving, and flexible thinking. While some children may start speaking slightly later, they quickly catch up and gain long-term cognitive advantages.
2. Do gut health and nutrition play a role in cognitive development?
Yes. A healthy gut supports brain function through the gut-brain connection, improving memory, focus, and mood. Foods like yoghurt, fruits, vegetables, and fish help maintain this balance, while too much junk food may harm a child’s learning and behaviour.
Make sure you foster a loving and happy environment at home that promotes learning and having fun. Children learn more easily when they’re relaxed, engaged, and happy. Time flies as they continue to learn and grow. It is truly an exciting time to be a parent when you see your child grow from a newborn to a toddler and beyond. Make learning an enchanting experience for your child and inculcate a love for learning and more. He will surely thank you after growing into an adult, as you witness his achievements and milestones hands-on, later in life.
References/Resources:
1. National Library of Medicine – Cognitive Development
3. Oklahama State University – 2.1 Cognitive Development: The Theory of Jean Piaget
5. Stanford University, DREME Network – What Children Know and Need to Learn about Shape and Space
6. Penn State Extension – Help Children Understand the Meaning of Counting
Also Read:
Major Stages of Child Development
Tips on Personality Development for Kids
Physical Development in Early Childhood
Social And Emotional Development In Children
Was This Article Helpful?
Parenting is a huge responsibility, for you as a caregiver, but also for us as a parenting content platform. We understand that and take our responsibility of creating credible content seriously. FirstCry Parenting articles are written and published only after extensive research using factually sound references to deliver quality content that is accurate, validated by experts, and completely reliable. To understand how we go about creating content that is credible, read our editorial policy here.















.svg)
















