Babinski (Plantar) Reflex – What it Is & its Importance
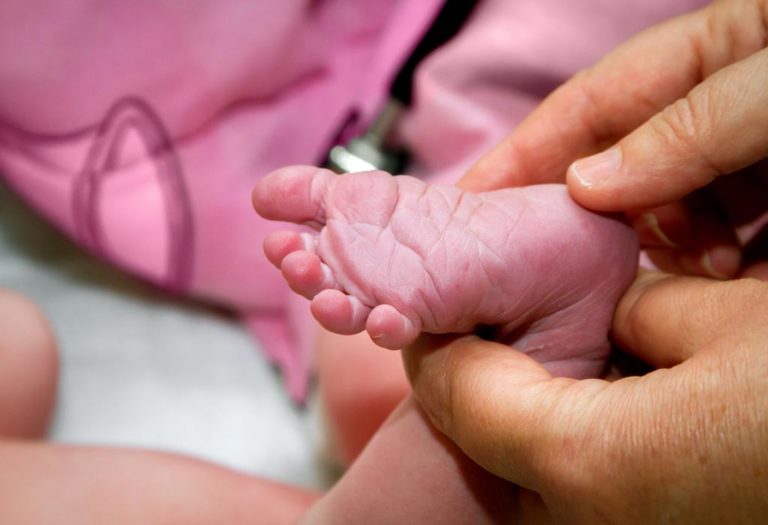
Identified by a French neurologist, Joseph Babinski, in the 19th century, Babinski reflex in newborn babies is also called Babinski sign or response. The medical term for this is the Plantar reflex. The Babinski or plantar reflex occurs when the sole of the baby’s feet is gently stroked. The feet are stroked from the heel to the toe’s base and on the lateral and outer sides of the feet. In response to the stroking, the big toe moves upwards while the remaining toes fan out. This reflex is seen at birth and stays up to 24 months. As a parent, it is essential to know such information to decide whether medical assistance is necessary or as the first diagnosis of any possible issue.
What Is Babinski Reflex and When Does It Occur?
The Babinski reflex is a reflex of the foot that happens in babies and young children. Generally tested by doctors, by stroking the sole, it is an essential tool the medical fraternity uses to ensure child activity in the brain, neurological responses, and nerve function are normal. It is a natural reflex that babies display when their foot sole is stroked, and their big toe bends upwards to the top of the foot while the other toes spread or flare out from one another (1).
The reflex is often tested with other natural reflexes to check for any neurological abnormalities. Some of the other reflex tests are (2):
Babinski reflex in infants is normal until the age of 2. The following are some typical timelines of its occurrence (3):
- It occurs in every newborn child.
- Sometimes, it could end by the time they turn a year old.
- If it is noticed beyond the age of 2, there is a likelihood of a neurological problem. It is not a normal finding in adults.
How to Check the Presence of Babinski Reflex?
The Babinski reflex is something that doctors check during routine visits to rule out any abnormality. While the doctors have their set of tools to test it, one can do it at home. As a parent, follow the instructions below to check for normal plantar reflex:
1. Gentle stroking
Hold the newborn’s feet and gently stroke the sole starting from the heel to the base of the large toe with your finger. The big toe will move upwards or in the top direction, while the other toes will spread out.
2. Using a reflex hammer
With the help of an object like a key or reflex hammer, the doctor will strokes the bottom of the foot from the heel to the base of the big toe.
3. Scraping an object along the foot sole
The doctor may scrape the object slowly at the bottom of the foot to get the baby to feel a gentle tickle.
4. Single-use testing kits
Single-use testing kits are used as an alternative to reflex hammers. Using these test kits on the baby’s foot can also help in checking the same.
5. Gently sticking object in the centre of the sole
Sticking a long stick into the toe blades can also help in checking for Babinski Reflex.
6. Conduct further tests to rule out false positives
Symptoms for Babinski may mirror the symptoms of a ticklish foot. So, the doctor may conduct further tests to test whether it is indeed a case of Babinski Reflex.
Causes of Babinski Reflex
If Babinski reflex is prevalent in children older than two years, it indicates a lack of integration in the corticospinal tract. Absent plantar reflex causes include tumours or injuries in the brain or spinal cord. If the corticospinal tract is well-integrated, the developed cells subdue the reflex in older children and adults. The presence of the Babinski reflex indicates damaged nerve cells in the tract, and the most general causes for an abnormal reflex are:
- Infections in the central nervous system like meningitis
- Tumour in the spine or brain
- Defects in spine, brain, or central nervous system
- Lou Gehrig’s disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Multiple sclerosis
- Spinal cord or brain injury
- In rare cases, an abnormal Babinski reflex occurs in babies due to congenital disabilities, such as sickle cell disease.
Importance of Babinski Reflex
A properly administered Babinski test will reveal a “positive or negative Babinski sign.” A sign of a healthy baby is the big toe pointing up and the other toes flaring up. The Babinski reflex remains until the baby matures.
The Babinski reflex in infants is the indicator of the health of a normal cortical spinal tract. The corticospinal tract is the nerve channel that transmits information between the brain, limbs, and body. It is responsible for the motor control function of the body and limbs.
When Does Babinski Reflex Stop?
About 60%-75% of newborns have the Babinski reflex as their nervous system develops after they are born. The reflex may not necessarily mean a neurological condition.
- The reflex response, which is common to infants, must be gone by 24 months of age. In some cases, the response disappears by the age of one.
- Doctors believe that the Babinski reflex in adults and children must not appear over the age of two, and if it does, it is abnormal. It could signify the sign of an underlying neurological condition that needs to be diagnosed.
What Does Positive and Negative Babinski Reflex Mean?
A positive Babinski reflex means that when the bottom of the foot is stroked, the big toe moves upward and the other toes fan out. This response is normal in babies under 2 years old because their nervous systems are still developing. However, in older children and adults, a positive Babinski reflex can be a sign of a problem with the brain or spinal cord, such as a stroke, multiple sclerosis, or a spinal injury (1).
A negative Babinski reflex is when the big toe stays still or moves downward, and the other toes may curl in. This is the normal response in older children and adults and shows that the nervous system is working as it should (1).
Other Tests for Babinski Reflex
When the Babinski test is hard to perform or gives unclear results, doctors can use other methods to check for the same reflex. Here are a few other tests your doctor can perform:
1. Oppenheim Test
In this method, firm pressure is applied along the medial side of the tibia (shinbone) from the knee to the ankle. If your big toe moves upward and your other toes fan out, it’s a sign the reflex is present.
2. Gordon Test
In this test, the doctor squeezes your calf muscles. If your big toe moves upward, it shows the same kind of reflex as in the Babinski test (4).
3. Chaddock Test
Here, the doctor strokes the outside of your foot, just below the ankle. If your big toe goes up and the other toes spread out, it’s another sign of a positive Babinski reflex (5).
What Is Abnormal Babinski Reflex and Why It Happens?
An abnormal Babinski reflex in children over two years of age indicates a lack of integration in the corticospinal tract. A well-developed corticospinal tract could be able to subdue the reflex in older adults and children. There could be a possibility of damaged nerve cells if the reflex persists in children over two years. A few conditions that could cause an abnormal Babinski reflex are:
- Presence of lesion in upper motor neuron
- Cerebral palsy
- Brain strokes
- Brain tumorus or brain injury
- Tumour or injury to the spinal cord
- Multiple sclerosis
- Meningitis
When Do You Need to See a Doctor?
If your baby shows a Babinski reflex after the age of two, then you may need to see a doctor. A paediatrician will be able to confirm if there is an underlying condition. If your child does not have any other developmental delays, it could just be a delay in integrating reflexes. The doctor may wait for a few weeks before confirming the same. If the reflex persists or the baby shows signs of neurological dysfunction, the doctor may conduct relevant tests to ascertain the possible underlying cause.
FAQs
1. Can the Babinski reflex be present in children over 2 years old?
In children over 2 years old, the Babinski reflex typically disappears as their nervous system matures. If it’s still present in a child beyond this age, it could suggest an underlying neurological issue and should be evaluated by a doctor.
2. Can you check the Babinski reflex at home?
While it’s possible to try the test at home, it’s not recommended to interpret the results without medical training. A healthcare professional is needed to properly evaluate the response and understand what it means.
3. What are the signs of Bilateral Babinski reflex?
The Bilateral Babinski sign involves an abnormal reflex response in both feet when the soles are stroked. In this condition, the big toes on both feet move upward, and the other toes fan out.
A very common reflex in children, the Babinski reflex, occurs because of a specific stimulus. Often checked by doctors to ascertain the child’s central nervous system, it tends to disappear by age two. It is advisable to get a physical examination for your child to check for any nervous disorders or neurological complications. If your doctor suspects an abnormal reflex, they may refer you to a specialist. Some conditions in children could display an abnormal Babinski reflex that cannot be cured. The causes for an abnormal reflex could be many, but early diagnosis of the symptoms could help in the treatment. Also, making appropriate changes to one’s lifestyle might help.
References/Resources:
1. Cleveland Clinic – Babinski Reflex (Plantar Reflex)
2. Stanford Medicine Children’s Health – Newborn Reflexes
3. National Library of Medicine – Babinski Reflex
4. National Library of Medicine – Gordon Reflex
5. National Library of Medicine – Chaddock Reflex
Also Read:
Startle Reflex in Newborn
Newborn Baby Reflexes
Stepping Reflex in Newborn
Was This Article Helpful?
Parenting is a huge responsibility, for you as a caregiver, but also for us as a parenting content platform. We understand that and take our responsibility of creating credible content seriously. FirstCry Parenting articles are written and published only after extensive research using factually sound references to deliver quality content that is accurate, validated by experts, and completely reliable. To understand how we go about creating content that is credible, read our editorial policy here.




















.svg)


















