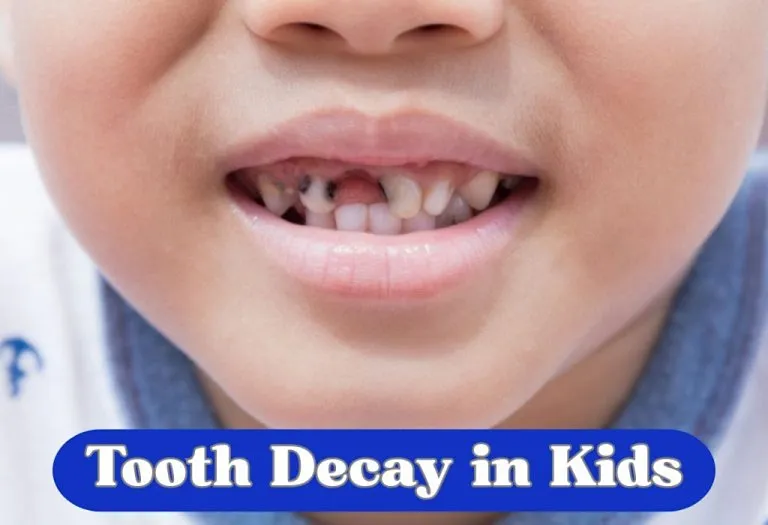
Tooth Decay (Caries or Cavities) in Kids: Causes, Signs, & Treatment

- What Is Tooth Decay in Children?
- What Causes Tooth Decay in Kids?
- Signs of Tooth Decay
- Diagnosis of Tooth Decay in Kids
- Treatments for Tooth Decay In Children
- How to Prevent Child Tooth Decay
- Does Making Changes in My Child’s Diet Help in Preventing Tooth Decay?
- Tips for Oral Hygiene
- FAQs
Children love sweets, chocolates, and other sugary treats, but these can sometimes make parents worry about their little one’s dental health. Tooth decay in children, also known as dental caries in children, occurs when harmful bacteria in the mouth produce acid that attacks the teeth. This process weakens the enamel and may eventually lead to cavities, causing pain, infections, and even tooth loss if untreated. Understanding the causes, signs, and treatments of tooth decay can help parents protect their child’s smile. Kids with tooth decay often face self-esteem and confidence issues later in their lives. Thus, it is essential to maintain proper dental hygiene from the beginning so that the likelihood of such issues is reduced.
What Is Tooth Decay in Children?
Tooth decay in children is a common dental problem in which the tooth’s surface (enamel) is damaged due to acid attacks from bacteria. When food particles, especially sugars and starches, remain on the teeth, bacteria feed on them and produce acids. Over time, these acids erode the protective enamel, leading to cavities (1).
If untreated, cavities can deepen, causing sensitivity, pain, and even infection in the surrounding tissues. Tooth decay doesn’t just affect the ability to chew but may also impact speech development, nutrition, and self-confidence in children. Early dental checkups and good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing and flossing, play a key role in preventing tooth decay.
What Causes Tooth Decay in Kids?
Every minute, a sticky layer called ‘plaque’ is formed naturally on the tooth. If we do not brush properly, the layer builds up. In addition, when we eat food, particles from the food get stuck in the teeth, adding bacteria in the mouth. These bacteria feed on the sugar made available from the food and produce acids. These acids attack the teeth, causing damage to the enamel, which results in tooth decay (2). Some of the causes of tooth decay are:
- Food Habits: Tooth decay in children is caused by changing food habits. Excessive sugar content in children’s food can affect their teeth. Children usually enjoy sweets, chocolates, ice cream, candies, biscuits, and other treats. They have a high sugar content and are typically sticky in nature. Moreover, the frequency of consuming these types of foods also plays a significant role. When eaten in excess, or when eaten frequently, i.e. multiple times a day, these foods make the teeth more susceptible to tooth decay.

- Drinks: The intake of juices, soft drinks, sports drinks, and flavoured milk can cause cavities as well. The kids who drink these beverages frequently are more prone to tooth decay as they are aerated and/or contain high sugar levels. The aerated drinks cause the enamel layer to erode, making it easier for bacteria to settle on, and the sugar provides the bacteria with food. Both of these factors cause cavities.
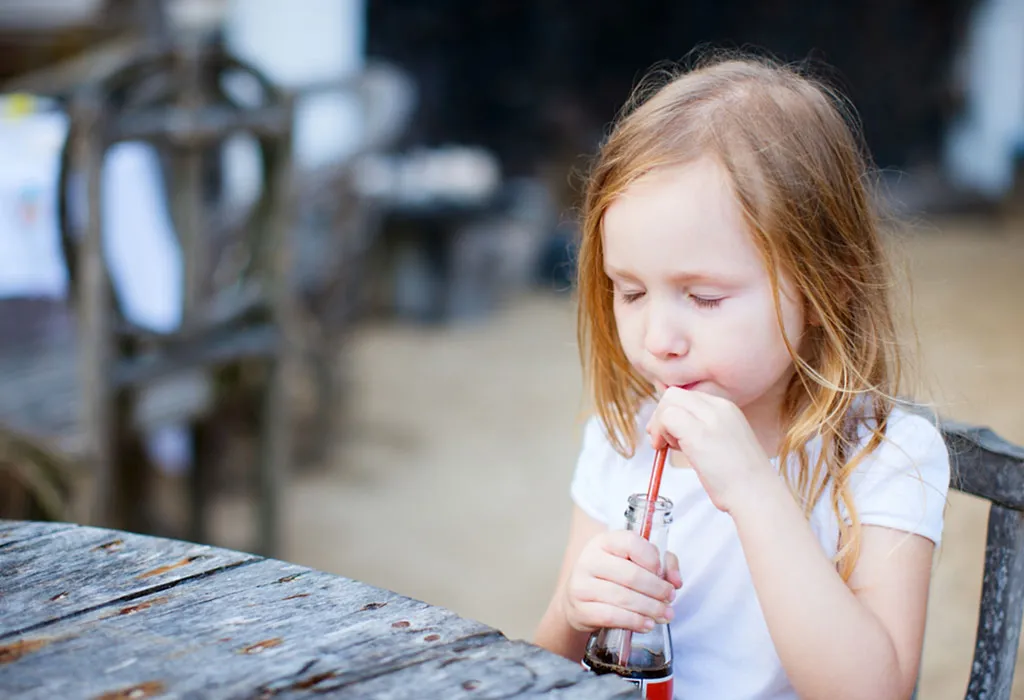

- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions can also increase the risk of cavities. If your child is suffering from chronic allergies, they may opt for mouth breathing, which can interfere with the flow of saliva. When the flow of saliva decreases, the mouth becomes dry. One of the many roles of saliva is to flush out bacteria that accumulate on the teeth. With a decrease in saliva, the chances of cavities increase.
- Bedtime Feeding: When infants are given milk bottles at night filled with milk, juice, and other sugar-containing liquids, these liquids sit on their teeth for hours, allowing bacteria to feed. The same can happen to toddlers when they drink from a sippy cup filled with these liquids.

- Deficiency of Fluoride: Fluoride is a natural mineral which helps in avoiding cavities and reverses the effect of tooth damage in the initial stage. This mineral is used in public water supplies, toothpaste, and mouth rinse. The availability of fluoride in home care and professional care in an adequate and timely manner can help prevent tooth decay.
Signs of Tooth Decay
Signs of tooth decay may not be experienced in the early stage. Here are some of them (3):
- Holes in teeth
- Change in colour of the teeth
- Sensitivity in teeth
- A toothache which occurs while eating or biting food items
- Recurrent pain during the day
- Spontaneous pain at night
- Bad breath
- Swelling of the gums
If your child is experiencing any of the above signs and symptoms, consult a pediatric dentist immediately. If you don’t get it treated, the decay will progress, leading to irreversible tooth damage.
Diagnosis of Tooth Decay in Kids
Dentists use different methods to check for early or advanced signs of tooth decay. Some common approaches include:
- Visual Examination: Checking for white spots, discolouration, or holes on the tooth surface.
- Dental X-Rays: Identifying hidden cavities or decay between teeth that are not visible to the naked eye.
- Exploring with Dental Tools: Using special instruments to detect soft areas on the enamel.
- Symptom Discussion: Asking parents and children about tooth pain, sensitivity, or chewing discomfort.
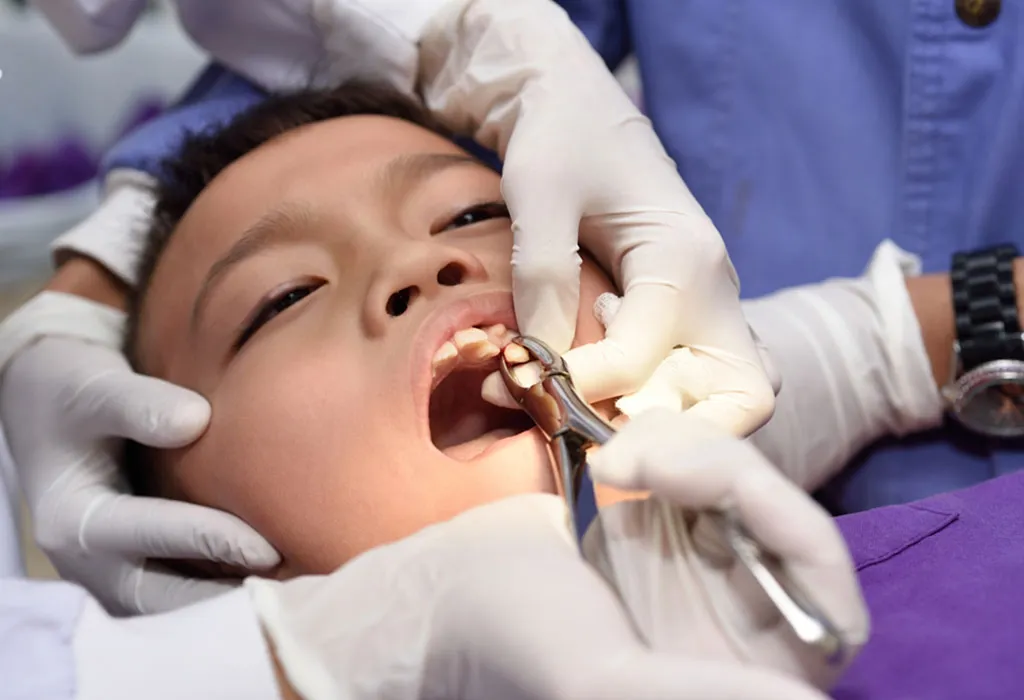
Treatments for Tooth Decay In Children
The treatment procedures for tooth decay depend upon the condition of the tooth. Frequent check-ups can help diagnose problems in their early stages and prevent severe damage. Several child tooth decay treatment options
options are available, such as the ones given below:
1. Fluoride Treatment
Fluoride treatment helps restore damaged enamel. Enamel damage is the initial stage of tooth decay, as you can see spots on the teeth during this stage. The fluoride gel or varnish is used to cover the spots and provide the necessary minerals for the teeth.
Fluoride toothpaste will be prescribed to repair the tooth and reverse the effect of the decay. Although fluoride is good for teeth, excess ingestion of fluoride during the development stage of teeth can cause changes in enamel structure, including dental fluorosis. Thus, the CDC recommends that children under 3 years of age should use a smear the size of a rice grain, and children above 3 to 6 years of age should use fluoride toothpaste not more than a pea-sized amount (4).
2. Fillings
Fillings are used to fill cavities that have progressed beyond the initial stage. The damaged portion is removed and filled with tooth-coloured or silver filling material. Fillings are composed of various materials, including dental amalgam and tooth-coloured composite resin or porcelain (5).
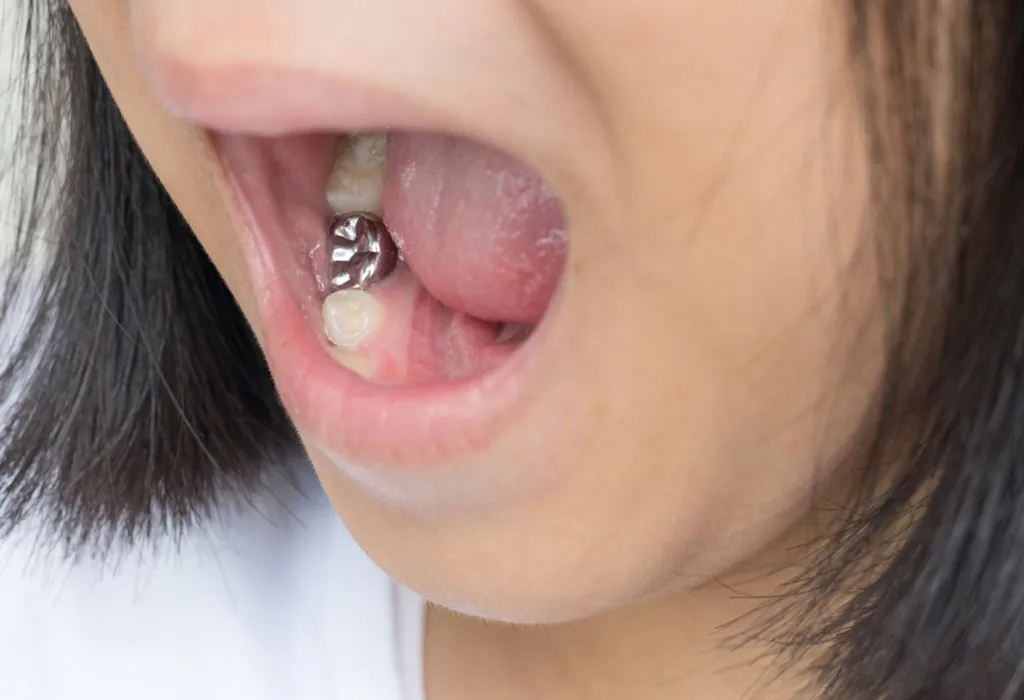
3. Crowns
Crowns are used for severely damaged teeth. In this procedure, the dentist drills and removes the decayed part and fills it with a filling material. Then an appropriately-sized crown, which is selected from a commercially available preformed crown kit, is fitted. The crown can be silver-coloured (stainless steel crowns) or tooth-coloured (zirconia crowns).
4. Root Canals
The tooth decay enters the inner layer of the tooth called the pulp. Once the pulp is damaged, root canal treatment must be performed. In this procedure, the infected pulp is removed and replaced with a medicament. Root canal treatment is followed by the placement of a crown to protect that tooth and restore its full function.
5. Teeth Extraction
If the tooth is damaged to the extent that it can’t be restored, it must be extracted. It may lead to further damage to the underlying permanent teeth if you ignore the issue. When a milk tooth is extracted, it should be followed by a space maintainer to keep the space for the permanent tooth if needed, as suggested by your pediatric dentist. If a permanent tooth is extracted, it has to be replaced with a suitable replacement.
How to Prevent Child Tooth Decay
Prevention of tooth decay in children can be done by following the methods suggested below (6) (7):
- Maintain your oral health during pregnancy, which will reduce the risk of transferring infections and promoting bacterial growth.
- Stop sharing spoons with your child. Infants don’t have any bacteria in their mouths from birth. By sharing spoons while checking the taste of food, you inadvertently transfer bacteria to your kid’s mouth.
- Experts recommend using silver diamine fluoride for young children with sensitive teeth, particularly those with developmental disabilities. This liquid medication is applied to cavities and helps slow down the growth of cavities quickly (8) (9).
- Use fluoridated water to protect your child’s teeth from infection. Drinking water contains this mineral naturally. If you are using non-fluoridated water, consult your dentist to get a supplement of fluoride.
- An infant’s mouth should be cleaned by wiping it with a clean and smooth cloth. Once they start developing teeth, clean them with a wet cloth or brush them with a soft baby toothbrush, using water (when the first few teeth come out) and then mild fluoride toothpaste.
- Don’t let your baby sleep with a bottle or food in their mouth. This will lead to exposure of teeth to sugars, resulting in infection and tooth decay.
- Don’t give your child sugary drinks like milk for long periods to drink from a sippy cup or bottle. Instead, give them water.
- Habituate your child to drink liquids from a cup or glass as early as possible after completing one year of age. Taking liquids from a cup or glass will decrease the risk of cavities.
- Regular brushing can help reduce the formation of plaque and germs in the mouth, which in turn lowers the risk of cavities. Habituate your child to brush twice a day, in the morning and at bedtime.
- Keep control of the sugary foods your child eats regularly. Foods like chips, candies, jellies, cookies, and fruit rolls contain sugars, and these foods pose a threat if consumed in excess.
- Consult your pediatric dentist when your child is one year old or when his/her first tooth erupts.
Does Making Changes in My Child’s Diet Help in Preventing Tooth Decay?
Some of the dietary changes that can be made include:
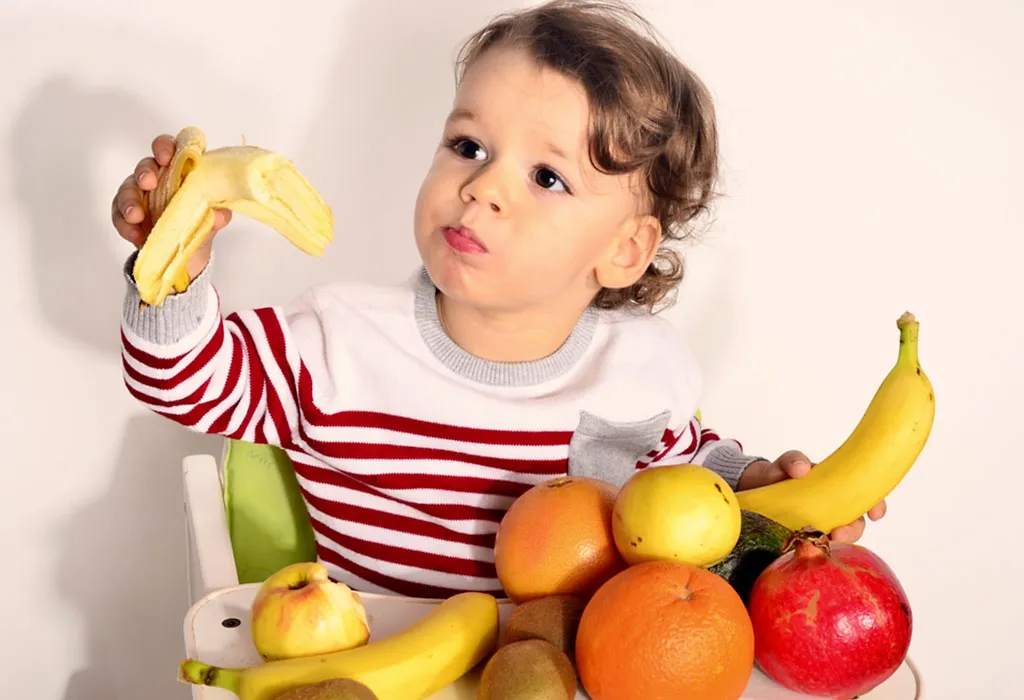
- Give fruits and vegetables to your child instead of carbohydrate-rich foods. Pears, melons, celery, and cucumbers are best to give as they are rich in fibre and low in sugar. Bananas and raisins contain sugars, so use them in limited quantities.

- Cheese can be added to your child’s diet plan as it helps stimulate the production of saliva. It can be given with the lunch items.
- Skip sticky and chewy foods as they are likely to spread bacteria in the mouth. If your child eats these foods, brush their teeth immediately afterwards.
Tips for Oral Hygiene
For healthy teeth, here are simple tips for oral hygiene.
- Regular Brushing
- Selecting a proper brush
- Regular flossing
- Using mouthwash
- Proper cleaning of the brush
- Changing your toothbrush after three months
- Using a tongue scraper to keep your tongue clean
- Stop frequent snacking
- Avoid sharing of utensils and cutlery with other children
- Avoiding foods with high sugar content
- Avoiding late-night snacking after they have brushed their teeth
- Taking your child to the dentist every three months if possible
FAQs
1. What causes tooth decay in children?
Tooth decay is mainly caused by bacteria in the mouth that produce acids after feeding on sugars and starches. Poor oral hygiene and frequent snacking on sweets increase the risk.
2. What are the early signs of tooth decay in kids?
White spots, tooth sensitivity, mild pain, or visible pits on the teeth are common early signs. Bad breath and discomfort while chewing may also indicate decay.
3. Who is at risk of tooth decay?
Risk factors, including poor oral hygiene, high levels of bacteria causing cavities, Water supplies with limited or no fluoridation, sugary and starchy diet, and reduced salivary flow in the mouth, can increase the risk of tooth decay in a child (10).
4. When should your child first visit the dentist?
The American Dental Association suggests a child’s first dental visit be after the appearance of their first tooth and no later than their first birthday (11).
5. Can cavities transmit from one person to another?
The Cleveland Clinic states that cavities are not contagious, but the bacteria that cause cavities can pass from one individual to another, for instance, from kissing, and lead to tooth decay and other dental issues (12).
Tooth decay may seem inevitable, but proper dental care and treatment can help your child maintain his dental health. Ensure you get your little one’s teeth checked by a good dentist, and teach him the importance of dental hygiene and health.
Also Read:
Braces for Kids Teeth
Broken Teeth in Kids
Common Teeth Problems in Children
Was This Article Helpful?
Parenting is a huge responsibility, for you as a caregiver, but also for us as a parenting content platform. We understand that and take our responsibility of creating credible content seriously. FirstCry Parenting articles are written and published only after extensive research using factually sound references to deliver quality content that is accurate, validated by experts, and completely reliable. To understand how we go about creating content that is credible, read our editorial policy here.
1. Johns Hopkins Medicine – Tooth Decay (Caries or Cavities) in Children
5. Mayo Clinic – Cavities and tooth decay
6. BetterHealth Channel – Tooth decay – young children
7. BetterHealth Channel – Dental checks for young children
8. American Academy of Pediatrics – Silver Diamine Fluoride to Stop Tooth Decay
9. NIH – Topical solution halts tooth decay in children
10. Children’s Hospital of Phildelphia – Tooth Decay (Caries or Cavities) in Children













.svg)
















