Polio Vaccination: Importance, Dosage, Side Effects and More

Polio vaccine is necessary for preventing the spread of poliovirus, which can lead to paralysis and, in severe cases, death. Recently, Tikrikilla, Meghalaya, reported a case of polio in a two-year-old child. Health experts have clarified that this case is due to a vaccine-derived strain, not the wild poliovirus, primarily affecting those with low immunity. This incident highlights the need to understand how polio vaccines work and the importance of proper dosing. Although the vaccine has successfully reduced polio worldwide, knowing its benefits, side effects, and the correct vaccination schedule is still essential.
Keep reading to learn about the different types of polio vaccines, their importance, and how to ensure complete protection against polio.
What Is Polio (Poliovirus) Vaccine?
The polio vaccine is an active immunisation agent that protects against poliomyelitis, a disease caused by the poliovirus. It works by helping the immune system produce antibodies against the virus. When a person receives polio shots, their immune system learns to recognise and fight the poliovirus if they are exposed to it in the future.
Also Read: Child Immunization & Vaccination Schedule
Is the Polio Vaccine Safe and Effective?
The vaccine is very safe, with only temporary side effects like redness and soreness at the injection site. Serious side effects are extremely rare. Years of research and use have confirmed that the vaccine is highly effective in preventing polio and has been essential in reducing and almost eradicating the disease worldwide (1).
Types of Polio Vaccine
There are two types of polio vaccines. These vaccines work differently and are used worldwide based on their effectiveness (2).
1. Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine (IPV)
This vaccine is made from killed or inactivated polioviruses. It is administered through an injection and helps protect against polio by stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies against the virus.
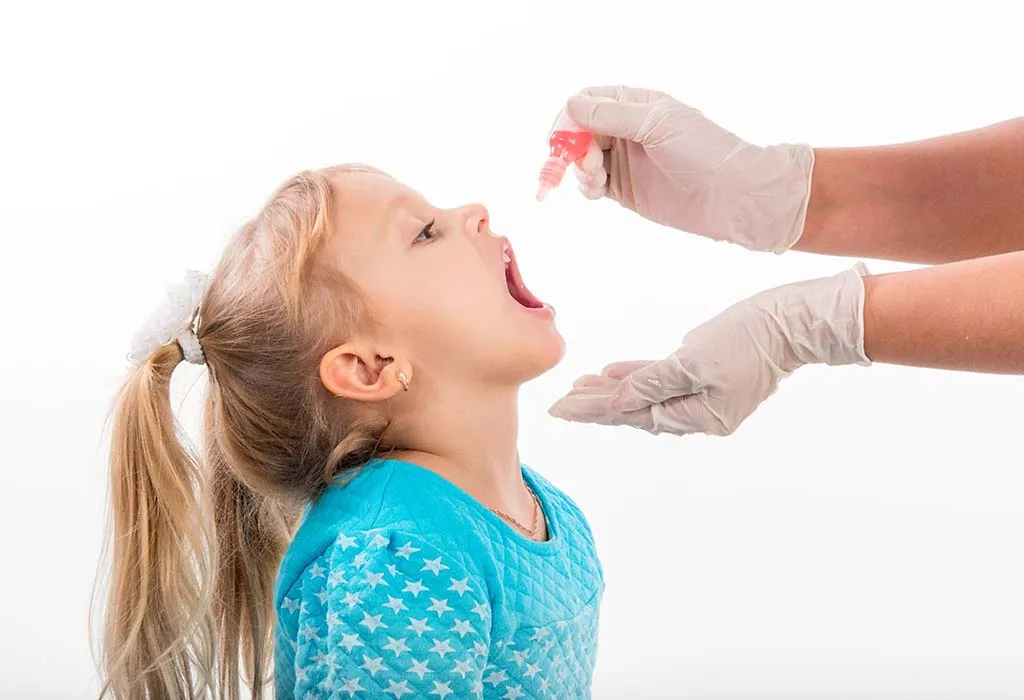
2. Oral Poliovirus Vaccine (OPV)
This vaccine is made from live, weakened polioviruses and is given orally, usually as drops. It is no longer licensed or available in the United States but is still used in many parts of the world.
Between the OPV and IPV, IPV has been the only polio vaccine in the United States since 2000 (3).
Who Should Get the Polio Vaccine?
The polio vaccine is vital for various groups of people to ensure protection against poliomyelitis. These include (4):
- Infants and young children should receive the polio vaccine in their routine immunisation schedule.
- Travellers who travel to regions where polio is still common.
- Laboratory workers who handle specimens that may contain polioviruses.
- Healthcare experts who are in close contact with patients infected with poliovirus.
When Should Children Get Polio Vaccination?
The recommended polio vaccine dose includes five shots of the Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV) or Oral Polio vaccine (5):
- First dose at 6 weeks
- Second dose at 10 weeks
- Third dose 14 weeks
- First booster dose at 18 months
- Second booster dose at 4-6 years
The schedule may vary in different countries, and you should follow as advised in your country.
How Is the Polio Vaccine Given?
The poliovirus vaccine is given in different ways depending on its type. The Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV) is given through an injection, typically in the leg or arm, depending on the patient’s age. On the other hand, the Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) is given orally, usually as drops.
Who Should Avoid the Polio Vaccine?
Certain people should avoid the polio vaccine or consult their doctors before receiving it (6):
- Those with a severe allergic reaction to any component of the polio vaccine.
- Those who have had a severe allergic reaction to a previous dose of the Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV).
Risk and Side Effects of Polio Vaccine
The polio vaccine is generally safe, though it may have minor and temporary side effects like swelling and redness at the injection site. In very rare conditions, OPV can lead to vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis (VAPP), a form of polio that results from the weakened virus in the vaccine mutating (7).
How to Care for Your Child After IPV Immunisation?
After your child receives the IPV immunisation, proper care can help ensure their comfort and well-being. Here are some steps to follow (8):
- Check for common side effects, these are temporary and should be resolved on their own.
- To alleviate soreness, you can apply a cool, clean cloth to the injection site. Medicines, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, may also be used, but consult your doctor for appropriate dosages.
- Allow your child to rest after the vaccination, especially if they seem tired or irritable.
FAQs
1. What should I do if my child misses a scheduled polio vaccine dose?
If a scheduled polio vaccine dose is missed, it is important to get back on track as soon as possible. Contact your doctor to reschedule the missed dose and ensure your child completes the vaccination series.
2. Can the polio vaccine be given with other vaccines?
Yes, the polio vaccine for babies can be given alongside other vaccines. It is commonly given as part of a combination vaccine schedule that includes other routine immunisations for children, such as those for diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (DTaP) or Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) .
3. What are the signs that indicate a serious reaction to the polio vaccine?
Severe reactions to the polio vaccine are rare but can include high fever, severe allergic reactions, or extensive swelling at the injection site. If any of these symptoms occur or if you notice any other unusual signs, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
Polio immunisation is crucial for fighting poliomyelitis and keeping us safe. The importance of timely and complete vaccination cannot be overstated, particularly in light of recent news about vaccine-derived polio cases. Stay informed about vaccinations to ensure a healthier future and contribute to the ongoing fight against polio.
References/Resources:
1. CDC – Polio Vaccine Effectiveness and Duration of Protection
2. Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia – Polio: The Disease & Vaccines
4. CDC – Polio Vaccine Recommendations
5. CDC – Routine Polio Vaccination
6. CDC – Contraindications and Precautions for Polio Vaccination
7. WHO – Polio Global Eradication Inititaive
8. Nemours KidsHealth – Your Child’s Vaccines: Polio Vaccines (IPV, OPV)
Also Read:
Pneumococcal Vaccine
Typhoid Vaccine for Kids
Flu Vaccine for Babies and Children
Childhood Vaccinations for Various Diseases
MMR Vaccine – Everything You Need to Know
Meningococcal Vaccination: Types, Schedule & Side Effects
Optional & Mandatory Vaccines for Babies and Children in India
Was This Article Helpful?
Parenting is a huge responsibility, for you as a caregiver, but also for us as a parenting content platform. We understand that and take our responsibility of creating credible content seriously. FirstCry Parenting articles are written and published only after extensive research using factually sound references to deliver quality content that is accurate, validated by experts, and completely reliable. To understand how we go about creating content that is credible, read our editorial policy here.













.svg)


















