Knee Pain in Children – Causes and Treatment
- Causes of Knee Pain in Children
- Symptoms of Knee Pain in Kids
- Diagnosis of Knee Pain in Kids
- Treatment of Knee Pain in Kids
- Tips to Prevent Knee Problem in Kids
- Home Remedies for Knee Pain in Kids
- When Should You Call the Doctor?
- FAQs
Knee problems are generally associated with the challenges of old age or with adults, in some cases. When a child complains about his hurting knee, we assume that the child has hurt his knee due to a fall while playing or jumping and that the pain will pass away in a few days. Children’s knee pain can be a concerning issue for parents, often requiring careful assessment to determine the best action for relief and recovery.
As you will read in this article, there are various severe causes of knee pain in children. As children grow, their body muscles, bones, and ligaments also grow in tandem, which is a natural process. However, in certain instances, all the parts of their body do not grow at the same rate, leading to growing pains generally felt in the leg or knee region.
Causes of Knee Pain in Children
Listed below are some of the common causes of knee pain observed in children:
1. Bacterial Infection
Bacterial infection in the knee region can cause pain and swelling, thus preventing the child from walking. If you observe any inflammation in or around the knee, the chances are there is a pus formation within the knee joints.
If the knee pain or swelling lasts for more than a day, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
2. Juvenile Arthritis
Juvenile arthritis can occur in children from 6 months up to 16 years. Warm or reddened knee joints, along with swelling around the joints, are an indication of juvenile arthritis. In teenage or pre-teenage children athletes, knee pain due to juvenile arthritis usually occurs in the knee’s anterior (or front) part. It is recommended to consult a doctor if you observe signs of this condition (1).
3. Osgood-Schlatter Disease
This common knee disease usually occurs in puberty-aged children or children who play sports. It causes knee inflammation where the shin bone attaches to the knee cap (2).
Along with medicines, proper rest is necessary for the child to recover from this knee disease.
4. Jumper’s Knee
This is another knee condition that affects the patellar tendon (the tendon that enables the knee to straighten up following jumping or squatting). Excessive jumping or squatting in active children can put severe pressure on the patellar tendon, thus causing injuries to the tendon fibres. Common symptoms of Jumper’s knee are swelling or pain right below the knee cap (3).
Children affected by this condition should stop all sporting or jumping activities until the swelling is reduced.
5. Soft Tissue Knee Injuries
Soft tissue knee injuries, which are common in physically active children, are caused by excessive use or pressure on the knee muscles, ligaments, and tendons. The RICE method, which comprises rest, ice packs, compression (using a bandage), and elevation, can speed up the healing of these injuries (7).
6. Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
Patellofemoral pain syndrome, or PFS or runner’s knee, occurs in the anterior part of the knee. Common among young teenagers and athletes, PFS is caused by excess weight pressure on the knee or kneecap displacement. Children with PFS experience knee pain when they squat, jump, or bend their knees. The RICE method is also useful for treating this condition. Consult a doctor if the pain persists or becomes severe (4).
7. Quadricep’s Tendinitis
Quadriceps tendinitis results from injury or strain to the quadriceps muscles in the knee. This condition is common in young teenagers who are involved in sports, such as football, athletics, or activities that involve a lot of running. Along with swelling and weakness, the affected child can experience pain in the lower thigh area, just above the patella (8).
Anti-inflammatory medicines and adequate rest can help the child recover from this knee condition.
8. Tumours
This is among the mildest forms of knee pain in children. Tumours are formed around the knee area and are usually the only symptom along with pain in the knee. You may need to diagnose this knee condition by looking for any abnormal growth of tissues. It is recommended to consult the doctor for a further plan of action.
If your child has knee pain, look for the symptoms that indicate a severe issue and seek medical attention immediately.
9. Meniscus Tears
Meniscus tears occur when the cartilage that cushions the knee joint is twisted or torn, often during sports activities. This injury can lead to pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the knee. Meniscus tears often require medical evaluation and may need surgical intervention (5).
10. Ligament Injuries
Knee ligament injuries, such as those affecting the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) or medial collateral ligament (MCL), can result from sudden stops or changes in direction during sports. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling, and instability in the knee joint (6).
Symptoms of Knee Pain in Kids
For almost 2 out of 5 kids, knee pain usually occurs due to growing pains, particularly during their growth spurt in pre-teen children. Growing pain usually results in aches in their legs, calves, thighs, and the back of their knees. Other common aches may be simply due to the amount of running, playing, and jumping most children are involved in. If your family has a medical history of restless leg syndrome (uncomfortable sensations in the legs), the chances are that your child may also have this condition.
If your child experiences more severe symptoms, it could be because they have a more serious knee condition than growing pains or aches. Here are some symptoms to watch out for that could indicate a bigger issue:
- Your child experiences pain in the thigh, calves, or posterior part of their knees throughout the day or the next morning.
- Severe swelling or inflammation in or around the knee joints.
- Your child experiences severe pain for a long time after sustaining a physical injury.
- Your child displays constant tiredness or weakness.
- Constant limping or the use of one particular leg for activities.
- Lasting signs of knee pain, such as unusual rashes around the knee region.
- Your child has a high fever, which can indicate Juvenile arthritis.
- Warm or severely reddened knee joints.
- Your child cannot fully move the knee, or the knee cannot support your child’s weight.
- Your child is experiencing constant locking of the knee, so your child cannot move.
Diagnosis of Knee Pain in Kids
According to Dr. Mark Halstead, a sports medicine specialist at St. Louis Children’s Hospitals, parents should not neglect all knee pain conditions in their children as simply growing pain. While growing pain is common in children aged 5-6, a teen or preteen can suffer from serious knee injuries, mainly if the child is active in physical sports.
According to Dr. Halstead, children involved in active sports like running and football or multiple sports are more susceptible to knee injuries. Stretching your knees before play or keeping ice on the knees after play can be useful techniques in preventing knee injuries (9).
Parents play a vital role in the initial response to a knee injury. While they may not be able to diagnose the injury specifically, they can provide crucial first aid before rushing their child to the hospital for a thorough diagnosis by a doctor. Read on to learn how you and the doctor can treat knee pain in kids.
Treatment of Knee Pain in Kids
In the case of a severe knee injury, you may observe the following in your child:

- Your child is unable to walk or bear his or her weight on the knees.
- Your child’s knee looks deformed.
- Your child experiences extreme pain.
- If the child has swelling and numbness near the knee region.
Here’s how to treat knee pain in a child: The immediate treatment should be to control the swelling around the knee using the RICE method discussed earlier. This comprises of rest, ice, compression, and elevation, as described below (10):
1. Rest the Knee
This includes resting your child and protecting the affected knee area.
2. Ice the Knee Region
This involves applying a cold pack of ice to the affected area to minimise the swelling. Keep applying the ice until the swelling subsides. Once the swelling is gone, apply heat to the same area. It is important to use a towel on the ice or heat pack and not apply it directly to the skin.
3. Compress the Knee With a Tight Wrap or Elastic Sleeve
Wrapping the swollen area with an elastic bandage can decrease the swelling. However, do not apply the compression too tightly, as this can cause more swelling.
4. Elevate the Knee
Elevate the affected knee with a pillow or soft cushion while you apply ice or use compression.
If your child’s knee is not swelling, you can also gently massage the knee region to alleviate the pain.
If your child is experiencing massive pain, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or medication can be used to provide pain relief and reduce swelling. Drugs such as Ibuprofen, Aspirin, and Naproxen are also consumed for immediate pain relief. However, such medication is not recommended for frequent or long-term use as there may be side effects. Ensure that you consult your doctor before administering any of these drugs to your child.
Knee pain can be painful and require your child to rest until recovery. This might make parents wonder whether there are ways to prevent knee problems in kids. The tips below may help you deal with your child’s knee issues.
Tips to Prevent Knee Problem in Kids
Strengthening the knee muscles and bones through exercise or physical therapy is one way to prevent knee problems in your child.
Listed below are additional tips for preventing knee injuries in children:
- If your child is overweight, helping him lose weight can reduce the body pressure on his knees and prevent injuries.
- For children active in physical sports, ensure they perform appropriate warm-up exercises, such as Hamstring and Quadriceps stretching, before and after the game. This can be followed by relaxing exercises after the workout.
- Daily exercises that strengthen the knee muscles and joints are a must for preventing knee pain. Aerobic exercises for children can also help build stronger leg muscles.
- Learning to bend the knees during jumping or any other physical activity can be very helpful.
- For children in athletics, the right sports shoes that provide support to the knee can be useful.
- Avoid physical activities such as running up (or down) the hill or deep knee bends, which put severe pressure on the knees.
- Regular training around the year can improve your child’s overall fitness and prevent common knee-related injuries.
Sometimes, home remedies can also be handy when treating knee pain if a doctor is not accessible.
Home Remedies for Knee Pain in Kids
In addition to the regular medication and therapy, you can try a few herbal remedies at home to ease the knee pain in your child. Listed below are some of the home remedies that you can use:
1. Applying a Cold Compress
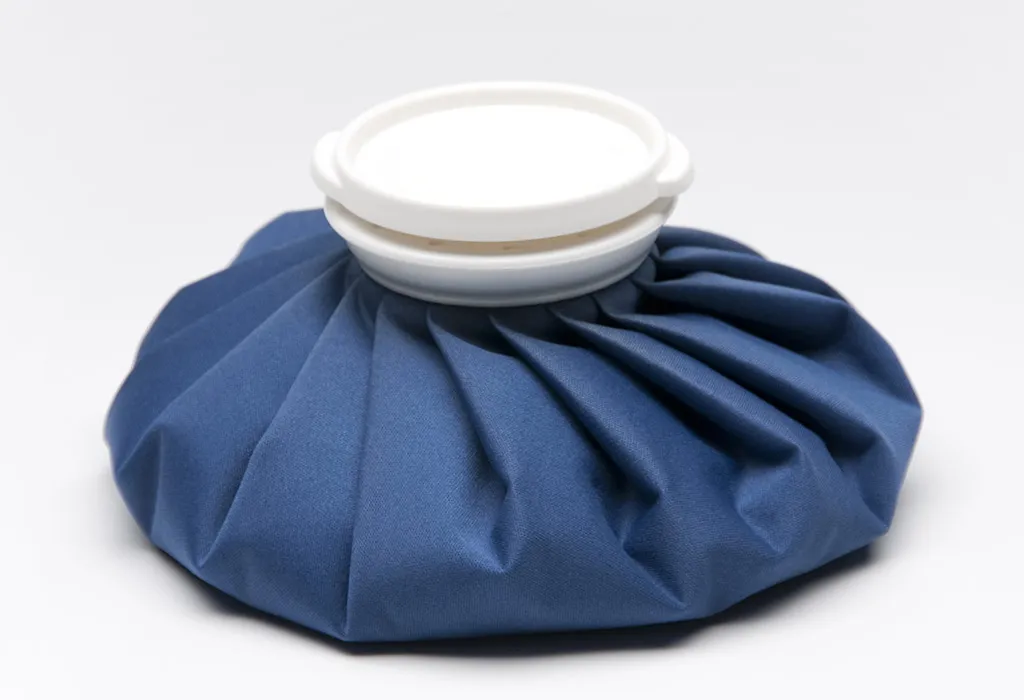

Applying a cold compress using ice cubes or a pack of frozen peas on the affected knee area reduces knee pain and swelling. The cold constricts the blood vessels, thus reducing blood flow to the affected area.
2. Willow Bark
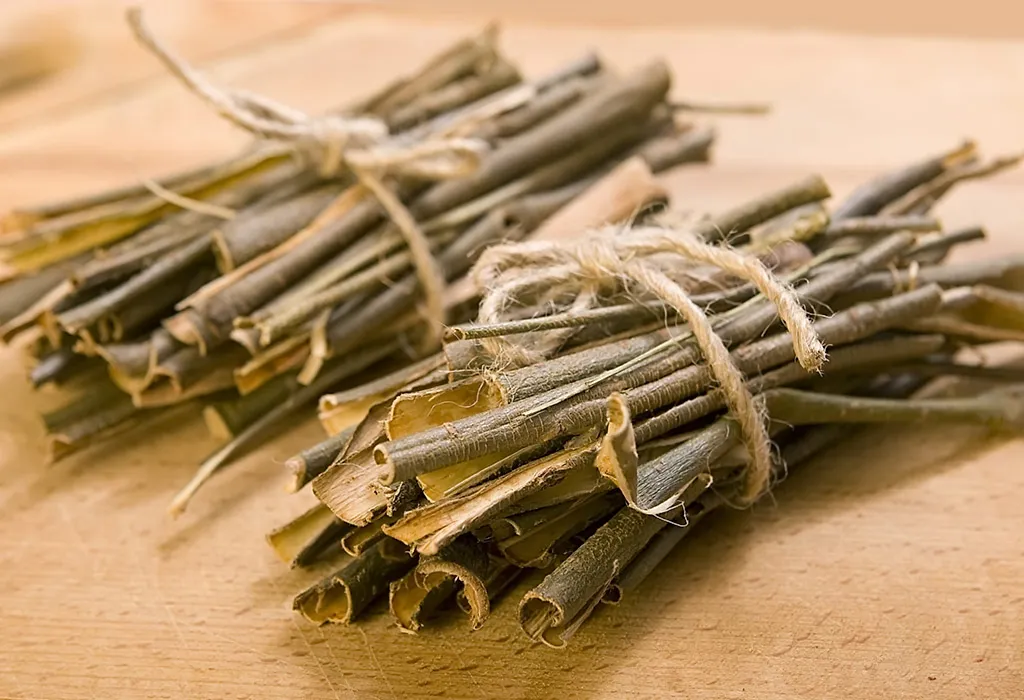

This common herb is regularly used to treat knee pain, particularly inflammation and fever. It is also known to have provided relief to patients suffering from arthritis. However, it should be used with caution, and if any red flags persist, you must consult a doctor immediately.
3. Ginger Extracts
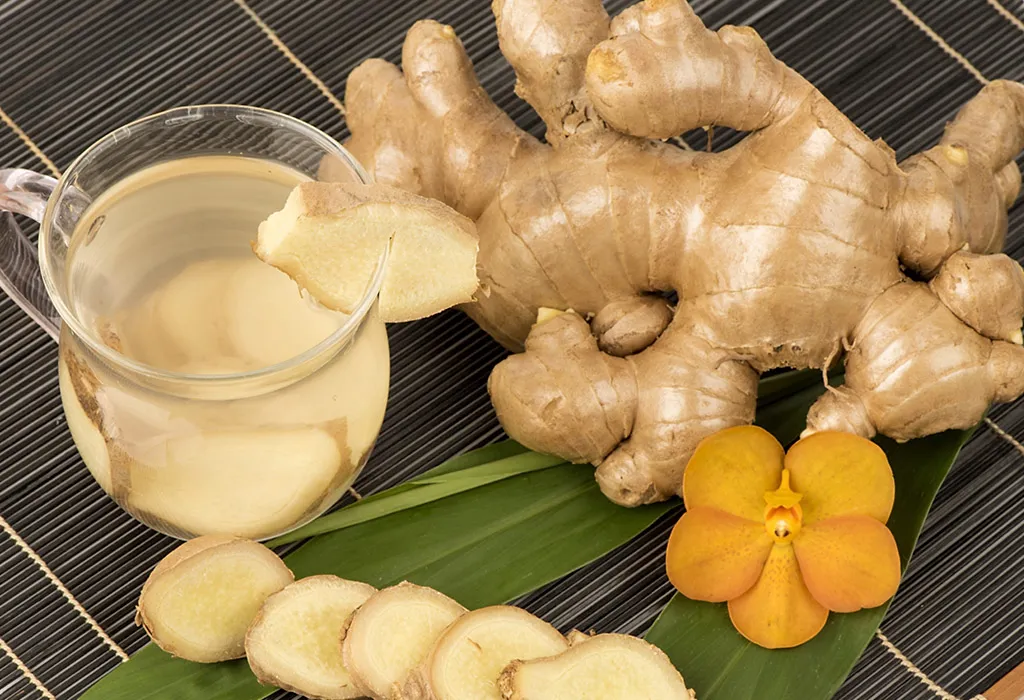

This remedy has also proven effective for pain relief for patients with arthritis. Ginger contains natural anti-inflammatory compounds that reduce swelling. For pain relief, you can massage the affected part with ginger oil 2-3 times daily. Ginger extracts can also be given along with anti-inflammatory medicines (12).
4. Apple Cider Vinegar

Apple cider vinegar is known to have alkaline properties that are useful in alleviating knee pains. Drinking 1-2 glasses of warm water mixed with half or one teaspoon of apple cider vinegar can remove the toxins around the knee region, thus bringing relief. It can also improve the flexibility of the knee movements by restoring the lubricants around the knee.
5. Cayenne Pepper

This natural herb contains Capsaicin, which is a natural reliever of pain. The natural pain-relieving properties of Capsaicin provide a warm sensation to the affected knee when applied externally, thus reducing the pain.
Recommended for anterior knee problems, you can make a paste of cayenne pepper powder and olive oil and apply it on the affected knee area each day. Alternatively, mix cayenne pepper with apple cider vinegar and apply the liquid to the affected area. You can also use a variety of ointments or gels containing cayenne pepper for immediate pain relief.
6. Mustard Oil

Massaging the knee with mustard oil can reduce pain and inflammation, as well as improve blood circulation in that part.
7. Turmeric

Turmeric is also an effective home remedy for knee pain. It contains the chemical curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Drinking a glass of hot water mixed with ginger and turmeric can help reduce knee pain.
8. Lemon

Lemon contains citric acid, which acts as a solvent for Uric acid crystals, one of the primary causes of arthritis. Thus, lemon is an effective home remedy for reducing knee pain.
Wrap a cotton cloth with 1-2 pieces of cut lemon, dip the cloth in sesame oil, and place the cloth on the affected part of the knee for 5-10 minutes. Alternatively, drinking warm lemon water early in the morning is also beneficial.
9. Other Herbal Ingredients

Other herbal ingredients, such as Epsom salt, fenugreek, and eucalyptus oil, are also known to be effective in relieving knee pain or injuries.
After trying these herbal remedies for mild knee pain, or if the child is in severe knee pain, it’s crucial to seek medical help. Let’s discuss in more detail when it’s necessary to consult a doctor.
When Should You Call the Doctor?
Children mostly hurt their knees when they fall while playing or bump their knees against a hard object. In such cases, most home remedies, or in certain cases, pain-killing medication or pain-relieving ointments or sprays, should be sufficient.
However, it is recommended to schedule a doctor’s visit if the knee pain was caused by immense force and is followed by (13):
- Severe swelling around the knee.
- Severe redness around the knee region.
- Significant pain.
- Tenderness or warmth around the knee joint.
- A popping sound at the time of the knee injury.
It is also advisable to call the doctor if a minor incident causes knee pain but leads to the following (9):
- Lasts for a long duration, particularly for the entire day.
- The child is limping or shows weakness in the knees.
- The child is unable to bear his or her weight.
- Interferes with the child’s sleep patterns.
- The pain is inhibiting the child’s normal activities.
FAQs
1. Can a child’s knee pain affect their physical activities or sports participation?
Yes, knee pain can significantly impact a child’s ability to participate in physical activities or sports. Pain may lead to decreased performance, reluctance to engage in certain activities, or even withdrawal from sports altogether. Parents and coaches need to recognise the signs of knee pain and provide the necessary support or adjustments to help the child remain active safely.
2. What are the long-term effects of untreated knee pain in children?
Untreated knee pain can lead to chronic issues, including joint instability, recurrent pain, and even long-term joint damage. Early intervention is crucial to address the underlying cause and prevent complications affecting the child’s physical activity and overall quality of life.
3. Are there any dietary recommendations to help with a child’s knee pain?
While diet alone may not directly alleviate knee pain, a well-balanced diet rich in nutrients can support overall joint health. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids (like fish), antioxidants (such as fruits and vegetables), and calcium can promote healthy bone and joint function. Staying hydrated is also crucial for maintaining joint health (11).
Knee pain is not just an irritant for an active child but can also be an indicator or precursor of long-term problems if not addressed in time. If your child complains of severe or frequent knee pain, it is advisable to see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
References/Resources:
1. Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA); National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases; https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/juvenile-arthritis
2. Osgood-Schlatter Disease; Nemours KidsHealth; https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/osgood.html
3. Jumper’s Knee; Nemours KidsHealth; https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/jumpers-knee.html
4. Bump. J. M, Lewis. L; Patellofemoral Syndrome; National Library of Medicine; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557657/
5. Meniscus tear (knee cartilage damage); NHS; https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/meniscus-tear/
6. Ligament Injuries to the Knee; The Johns Hopkins Medicine; https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/ligament-injuries-to-the-knee
7. Soft Tissue Injuries; Sports Medicine Australia; https://sma.org.au/resources/injury-fact-sheets/soft-tissue-injuries/
8. King. D, Yakubek. G, Chughtai. M, et al.; Quadriceps tendinopathy: a review-part 1: epidemiology and diagnosis; PubMed Central; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6409230/
9. Knee Pain in Kids; St. Louis Children’s Hospital; https://www.stlouischildrens.org/health-resources/pulse/knee-pain-kids
10. Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (RICE); University of Michigan Health; https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/tw4354spec
11. Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Your Health; Arthritis Foundation; https://www.arthritis.org/health-wellness/treatment/complementary-therapies/supplements-and-vitamins/omega-3-fatty-acids-for-health
12. Altman. R. D, Marcussen. K. C; Effects of a ginger extract on knee pain in patients with osteoarthritis; PubMed; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11710709/
13. 8 Signs Your Child’s Knee Needs To Be Examined; Nationwide Children’s Hospital; https://www.nationwidechildrens.org/specialties/sports-medicine/sports-medicine-articles/8-signs-your-childs-knee-needs-to-be-examined
Also Read:
Neck Pain in Kids
Groin Pain in Children
Foot Pain in Children
Swollen Lymph Nodes in Kids
Irritable Bowel Syndrome in Children
Was This Article Helpful?
Parenting is a huge responsibility, for you as a caregiver, but also for us as a parenting content platform. We understand that and take our responsibility of creating credible content seriously. FirstCry Parenting articles are written and published only after extensive research using factually sound references to deliver quality content that is accurate, validated by experts, and completely reliable. To understand how we go about creating content that is credible, read our editorial policy here.












.svg)
















