Jaundice in Children – Causes, Symptoms & Treatment

- What Is Jaundice?
- Types of Jaundice
- Causes of Jaundice in Newborns
- Causes of Jaundice in Children
- Symptoms of Jaundice in Kids
- Risk Factors of Jaundice in Kids
- Diagnosis of Jaundice in Children
- Treatment of Jaundice in Children
- Complications of Jaundice in Children
- Home Remedies for Jaundice in Kids
- Diet for Children Suffering From Jaundice
- How to Prevent Jaundice in Children?
- When to Call the Doctor
- FAQs
Most parents recognise the fear and trepidation that comes with their child falling severely ill. It can be one of the most frightening things a person can go through. Not knowing about the condition also adds to this fear. This can change, as learning about an illness can not only alleviate your concerns but also help you provide the best care possible for your child. One of the conditions that can affect numerous kids worldwide is jaundice in children. It is an illness that affects the bloodstream, liver, digestive, and excretory systems of the body. This condition is easy to identify as it will turn your child’s skin and sclerae (the white part of the eyes) yellow. Jaundice can affect adults as well as kids.
What Is Jaundice?
Amongst the numerous conditions that can affect your child, one of the easiest illnesses to identify is jaundice. Although jaundice alone is not a dangerous illness, the yellowing of the skin and the white part of the eyes is a sign of a rise in bilirubin in the bloodstream (1). Bilirubin, commonly known as bile, is a yellow fluid that is produced in the liver and is the end product of red-blood-cell (haemoglobin) breakdown. This fluid is essential to the functions of the body, particularly the digestive tract. This fluid usually helps regulate the digestive system and is excreted through the stool. When it fails to be excreted and begins to work its way into your system, it can spike the amount of bilirubin in the blood, which leads to a condition known as hyperbilirubinemia. This is the primary cause of the change in the colour of a person’s eyes and skin.
Types of Jaundice
Here are some different types of jaundice in children.
1. Obstructive Jaundice
This type of jaundice is caused when the natural excretion of bile from your body is blocked, causing extra bile to be present in your liver.
2. Pre-Hepatic Jaundice
Also called haemolytic jaundice, this is caused when the red blood cells break down much faster than they should. Red blood cells have bile particles in them, and when they break down too fast, it can cause excess bile in your body.
3. Hepatocellular Jaundice
Commonly called intra-hepatic jaundice, this is caused due to some form of trauma or injury that damages the liver, causing a large amount of bile to be present in your body.
Causes of Jaundice in Newborns
- Physiological hyperbilirubinemia
- ABO incompatibility
- Rh incompatibility
- Cephalhematoma
- G-6-PD deficiency, Crigler-Najjar syndrome, Gilbert Syndrome
- Biliary atresia
- Choledochal cysts
- Hepatocellular causes
- Intrauterine infections
- Metabolic causes
- Breast milk jaundice
- Neonatal Sepsis
- Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN)
- Hypothyroidism
- If your baby is born premature, jaundice is common. This is because the liver is still developing, and the bilirubin isn’t flushed out of the system. This should correct itself in a few weeks.
Causes of Jaundice in Children
Jaundice in children is a common condition characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes due to elevated bilirubin levels. It can result from various causes as follows:
- Malaria
- Sickle cell crisis
- Spherocytosis
- Thalassemia
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD)
- Drugs or other toxins
- Autoimmune disorders
- Neonatal Hepatitis
- Alagille Syndrome
- Cystic Fibrosis
Symptoms of Jaundice in Kids
There are many ways to identify jaundice, some of the symptoms of this condition are:
- The skin and the white part of the eyes turn yellow
- Frequent high fevers
- Extremely itchy skin
- Pale stool or yellow-colored stool
- Dark urine
- Fatigue accompanied by other illnesses
- A rapid loss of weight
- A constant bitter taste in your child’s mouth
- Chills accompanied by some of the other symptoms
- Abdominal pain
- Joint pains with other signs
- Weakness
- Loss of appetite
Risk Factors of Jaundice in Kids
Jaundice in children can be influenced by various risk factors that contribute to the elevated levels of bilirubin in their bloodstream. Understanding these factors is crucial for early identification and appropriate management. Here are some key risk factors associated with jaundice in children:
- Premature Birth: Infants born prematurely may have underdeveloped liver function, increasing their susceptibility to jaundice.
- Blood Type Incompatibility: ABO or Rh incompatibility between the blood types of the mother and the baby can lead to hemolysis, causing jaundice.
- Sibling History: If an older sibling had jaundice, there might be a higher risk for subsequent siblings.
- Infection During Pregnancy: Maternal infections, especially during the early stages of pregnancy, can contribute to jaundice in the newborn.
- East Asian or Mediterranean Descent: Certain ethnic backgrounds, such as East Asian or Mediterranean, have a higher prevalence of conditions like G-6-PD deficiency, which can result in jaundice.
- Cephalhematoma or Bruising During Birth: Trauma during birth, such as cephalhematoma or excessive bruising, can lead to increased breakdown of red blood cells and subsequent jaundice.
- Breastfeeding: Breastfed infants may experience prolonged jaundice due to factors in breast milk that can interfere with bilirubin elimination.
- Diabetes in the Mother: Infants born to mothers with diabetes, particularly gestational diabetes, are at an increased risk of developing jaundice.
- Liver Diseases or Conditions: Certain congenital liver diseases or conditions can contribute to impaired bilirubin processing, leading to jaundice.
- Certain Medications: The use of specific medications during pregnancy or in the neonatal period may increase the risk of jaundice in infants.
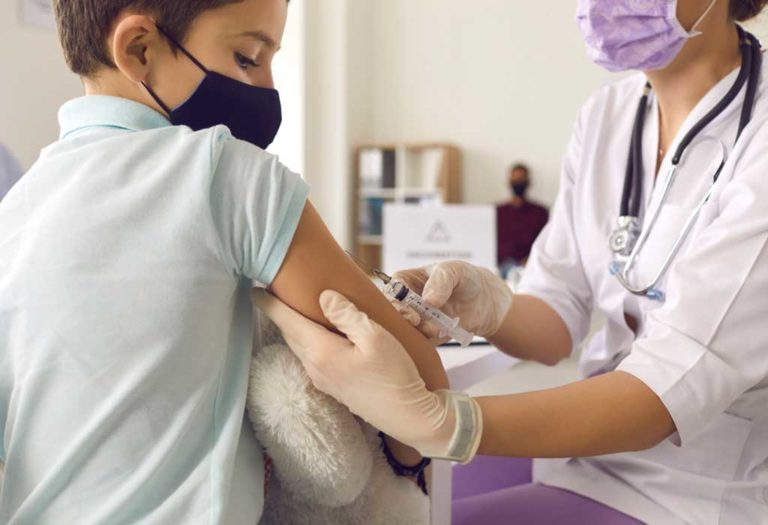
Diagnosis of Jaundice in Children
Diagnosing jaundice can be done in different ways. The tests to be taken up will depend on the physical examination findings. Here are some other things your doctor may ask you to do to confirm the diagnosis (2).
- Get an ultrasound abdomen done to check liver size, echotexture, bile duct lumen and the extrahepatic system
- Doctors may ask you to do an LFT. This is a liver function test, usually, a blood test that can help evaluate the levels of bilirubin in the blood (3).
- The lab may take samples for a complete blood count, haemoglobin count, peripheral smear, reticulocyte count. These routine tests help doctors diagnose jaundice.
- Routine urine sample to test the urobilinogen in your urine.
- Bilirubin tests- both direct and indirect bilirubin to detect the presence of bilirubin in your child’s blood.
- At times, doctors can diagnose a child by doing a physical examination where they check for swelling in the feet, legs, and ankles. All these indicate cirrhosis of the liver .
- If suspected Wilsons disease may get Serum copper levels and serum Cerulopasmin levels.
- In some cases, a liver biopsy may be recommended to assess the extent of liver damage and determine the underlying cause of jaundice.
- If there is a suspicion of a genetic or hereditary liver disorder, genetic testing may be conducted to identify specific gene mutations or abnormalities.
Treatment of Jaundice in Children
Whether you’re treating a four-year-old child suffering from jaundice or an adult, the patient must get sufficient rest, and increase the intake of fluids. In most cases, this should cure the condition, and in the cases, it doesn’t, here are a few other treatments (4):
- If jaundice is causing hepatitis, anti-viral medication could be prescribed by Doctor to help combat the condition.
- In the case of blockage of the bile ducts, your child may need surgery.
- In cases of sickle cell anaemia or thalassemia, a complete blood cell replacement procedure may be required.
- If jaundice is caused by Gilbert Syndrome, the treatment, if any, is minimal and varies from doctor to doctor.
- Jaundice caused due to a weak liver condition cannot be fixed. Doctors, in this case, may advise a change of diet and lifestyle to help slow down the deterioration of the liver.
- For cases of neonatal jaundice, especially when caused by physiological factors or conditions like ABO or Rh incompatibility, phototherapy may be recommended. This involves exposing the baby to a special type of light that helps break down bilirubin in the skin.
- In situations where dehydration is contributing to jaundice, especially in newborns, the administration of intravenous fluids may be necessary to ensure proper hydration and promote the elimination of bilirubin.
Talk to your physician to come up with a customised treatment plan to help you combat this condition.
Complications of Jaundice in Children
Frequently, jaundice is a temporary and generally non-threatening condition. However, in uncommon instances, it can become severe, and in rare cases, life-threatening. Thankfully, timely intervention can avert the majority of complications associated with jaundice in children.
Without appropriate treatment, jaundice has the potential to result in significant health challenges. Elevated bilirubin levels, if left unaddressed, can inflict harm on cells throughout the entire body. Severe jaundice poses the risk of causing brain damage, known as kernicterus, which may lead to complications like cerebral palsy or deafness.
Home Remedies for Jaundice in Kids
Apart from the medicated treatments, some parents may choose to opt for natural home remedies. Here are a few remedies that may help combat jaundice.
1. Tomatoes
Rich in enzymes called lycopene that repair damaged liver, it is believed that tomatoes have properties that can help rid your child of jaundice (5).

Image Credit : AI Generated Image
2. Turmeric
This ingredient reinforces enzymes that flush out carcinogens that hurt the liver and can help beat jaundice in kids (6).

Image Credit : AI Generated Image
3. Sugarcane Juice
It is estimated that apart from helping restore glucose, sugarcane has particular properties that can fasten recovery from jaundice.

Image Credit : AI Generated Image
4. Buttermilk
Not only does buttermilk re-energise and refresh your child, but it also hydrates them and helps improve digestion. This can help combat jaundice.

5. Barley Water
Considered the quickest natural cure for jaundice, it is assumed that barley water has properties that improve the functioning of the digestive tract and liver.

Image Credit : AI Generated Image
6. Lemon and Beetroot Juice
Lemon juice works to protect the liver, and beetroot has properties to purify the blood and help digestion. The combination of the two can help cure jaundice quickly and efficiently.

Image Credit : AI Generated Image
7. Papaya Leaf Juice
Papaya leaf juice is believed to have properties that can help in improving liver function and aiding in the recovery from jaundice.

Image Credit : AI Generated Image
8. Carrot Juice
Carrot juice is rich in antioxidants and vitamins, which are beneficial for overall liver health. It is thought to support the liver in the recovery process from jaundice.

Image Credit : AI Generated Image
Diet for Children Suffering From Jaundice
During jaundice, it is essential to regulate your child’s diet religiously. This is because this condition can cause weakness and fatigue. Here are a few things to keep in mind while creating a meal plan for a child suffering from jaundice:
- Hydration is the key. This illness will dehydrate your child rapidly, ensure they stay well hydrated throughout the day.

- Keep the meals short and frequent; this will keep their energy levels up without overloading their system. This also will help digestion
- Fresh fruits and vegetables should be consumed.
- Give your kids carb-rich food with no oil or fat.
- Avoid refined sugar and saturated fat found in animal fat.
- If your child has low energy levels give them a glucose supplement.
- Incorporate lean protein sources such as poultry, fish, legumes, and tofu to support muscle maintenance without putting excessive strain on the liver.
- Opt for whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread, as they provide essential nutrients and fiber while being gentle on the digestive system.
- Consider dairy alternatives like almond milk or soy milk as they are lighter on the digestive system compared to full-fat dairy products.
- Introduce small amounts of healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and seeds to provide essential fatty acids without overburdening the liver.
- Steer clear of spicy and fried foods as they can be harsh on the digestive system and may exacerbate discomfort during jaundice recovery.
- Foods high in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers, can aid in the absorption of iron and promote overall immune health.
Talk to a dietician and a doctor before implementing a diet plan.
How to Prevent Jaundice in Children?
Here are a few tips to help prevent jaundice:
- Make sure your kids stay hygienic.
- Ensure your kids drink mineral or bottled water or boil the water before drinking it.
- Eat fresh food, and have a balanced diet.
- Ensure your kids get their vaccines.
- If possible, promote breastfeeding, as breast milk provides essential nutrients and antibodies that can enhance the child’s immune system and reduce the risk of infections.
- Ensure pregnant women receive appropriate prenatal care to prevent infections that could be transmitted to the baby during childbirth, leading to jaundice.
- In areas where malaria is prevalent, take measures to prevent mosquito bites and provide appropriate anti-malarial interventions to reduce the risk of malaria-induced jaundice.
- Administer medications to children as prescribed by healthcare professionals and avoid self-medication. Improper use of medications can sometimes contribute to liver damage and jaundice.
We recommend you talk to your doctor for more tips on how to prevent jaundice.
When to Call the Doctor
Jaundice in children, especially newborns, is often harmless but can sometimes indicate a serious underlying condition. Parents and caregivers should watch for the following warning signs and consult a doctor if they occur:
- Jaundice in the first 24 hours
- Worsening or persistent jaundice
- Poor feeding or lethargy
- Dark urine or pale stools
- High-pitched crying or fever
FAQs
1. Does jaundice in kids disappear on its own?
In many cases, jaundice in kids resolves on its own without the need for specific treatment. Physiological jaundice, common in newborns, typically diminishes as the baby’s liver matures and is often considered a normal part of development. However, if jaundice persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
2. Can teething or viral infections trigger jaundice in toddlers?
While teething itself doesn’t cause jaundice, certain viral infections (e.g., Epstein-Barr virus or hepatitis A) can lead to liver inflammation and jaundice in older kids. If jaundice appears alongside fever, fatigue, or abdominal pain, a doctor should rule out infections or liver issues.
3. Does jaundice in kids always mean a liver problem?
Jaundice in kids doesn’t always mean a liver problem—it can also result from blood disorders (like hemolytic anemia), infections, or metabolic conditions. While liver issues (hepatitis, biliary atresia) are common causes, harmless newborn jaundice often stems from an immature liver.
Jaundice can be a tough disease to face. It can exhaust your kids and you. Remember, with the right treatment and care; they can make a complete recovery. It is highly recommended that you follow through with a treatment plan for the entire prescribed duration, and ensure that proper hygiene is maintained. Diet and exercise with good hygiene can help avoid diseases like jaundice.
References/Resources:
2. Boston Children’s Hospital – Jaundice
3. National Library of Medicine – Jaundice
4. Nationwide Children’s Hospital – Jaundice in Children
6. NICS Well – Can curcumin slow liver disease?
Also Read:
Encephalitis in Kids
Kawasaki Disease in Kids
Measles(Rubeola) in Children
Rheumatic Fever in Children
Was This Article Helpful?
Parenting is a huge responsibility, for you as a caregiver, but also for us as a parenting content platform. We understand that and take our responsibility of creating credible content seriously. FirstCry Parenting articles are written and published only after extensive research using factually sound references to deliver quality content that is accurate, validated by experts, and completely reliable. To understand how we go about creating content that is credible, read our editorial policy here.














.svg)
















